




Since the beginning of the year, there has been a hot topic in the automotive industry. An Arctic cold wave caused several electric vehicles to discharge in a region of the United States where temperatures dropped below -30 degrees Celsius. What’s more, the rapid drops in battery capacity led to situations in which drivers were unable to reach a charging station and ended up being towed due to a dead battery.
However, not all electric vehicles were in disarray. Hyundai Motor Group’s electric vehicles were able to charge during this intense cold wave as they were designed to handle even extreme cold weather. The industry is analyzing this phenomenon, and attributes it to differences in how manufacturers design for extremely cold conditions. What differences really determined these results? Let’s take a look at Hyundai Motor Group’s electric vehicle battery technology that enables their batteries to charge without a hitch in the coldest conditions.
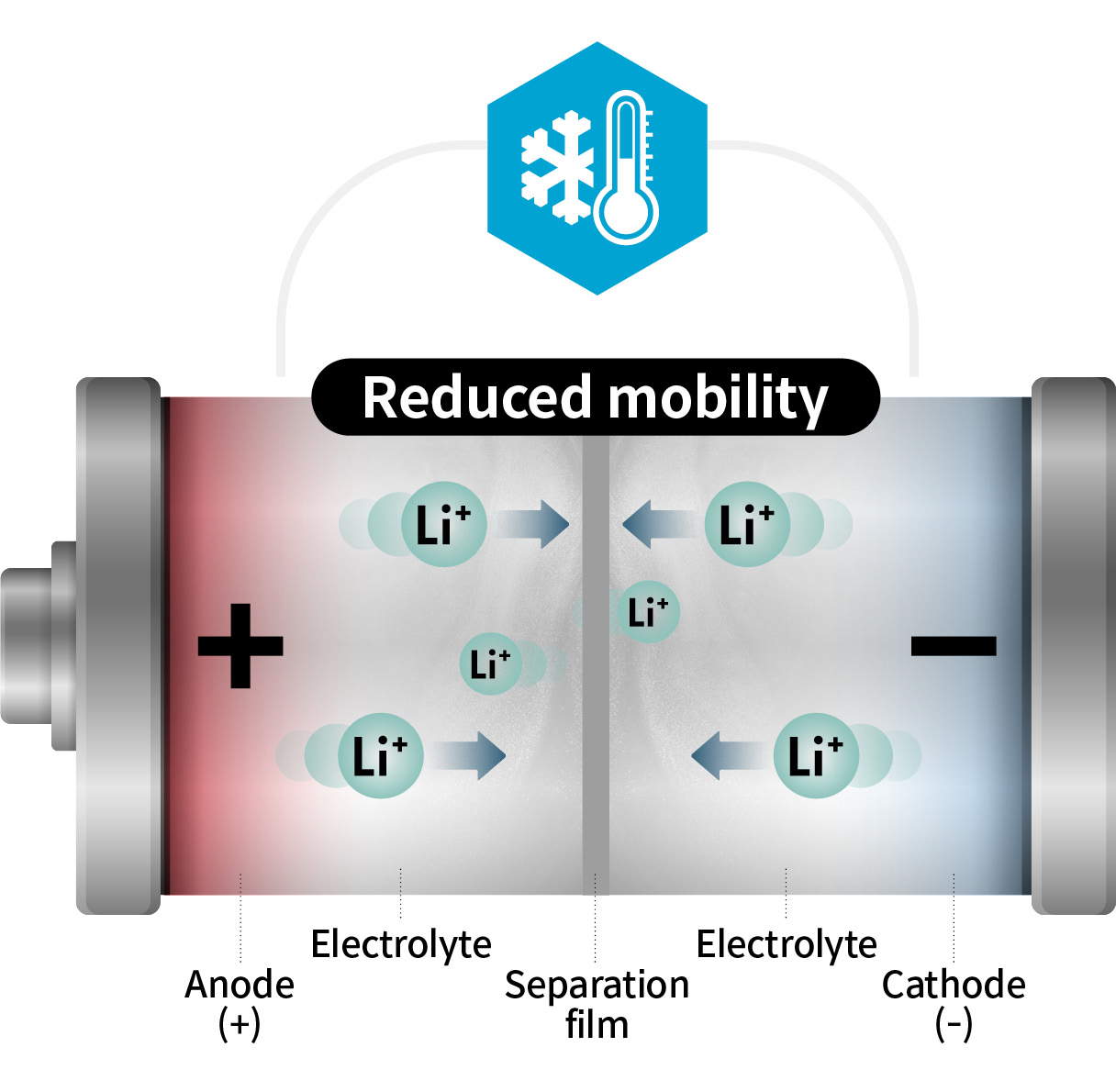
You’ve probably experienced your smartphone’s battery draining faster than usual in extremely cold weather. Like this, cold weather affects battery drain. This is easy to understand once you know how batteries charge and discharge.
Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles, charge and discharge by moving lithium ions back and forth between the anode and cathode in the internal electrolyte. However, as the temperature drops, the lithium ions also move slower between the anode and cathode. This is because the resistance of the electrolyte increases as the internal temperature decreases. Eventually, the battery isn’t able to perform as well as it should, charging slower and draining faster than usual.
Electric car batteries typically perform optimally around 25-35 degrees Celsius. In fact, this temperature is where you’ll find the fastest charging speeds and highest mileage. Electric vehicle manufacturers are always applying thermal management technologies to maintain the right temperature levels for optimal battery performance. Some examples of this are heating the battery in cold weather, or using a cooling system to reduce the heat of the battery that’s become too hot.
The most widely used technology for raising the temperature of the battery to the optimal range in the winter is to add a heater directly to the battery pack. Some manufacturers use existing motors and inverters to raise the coolant temperature to warm up the battery. These technologies not only raise the temperature of the battery but also maintain the optimal temperature for the highest battery performance.
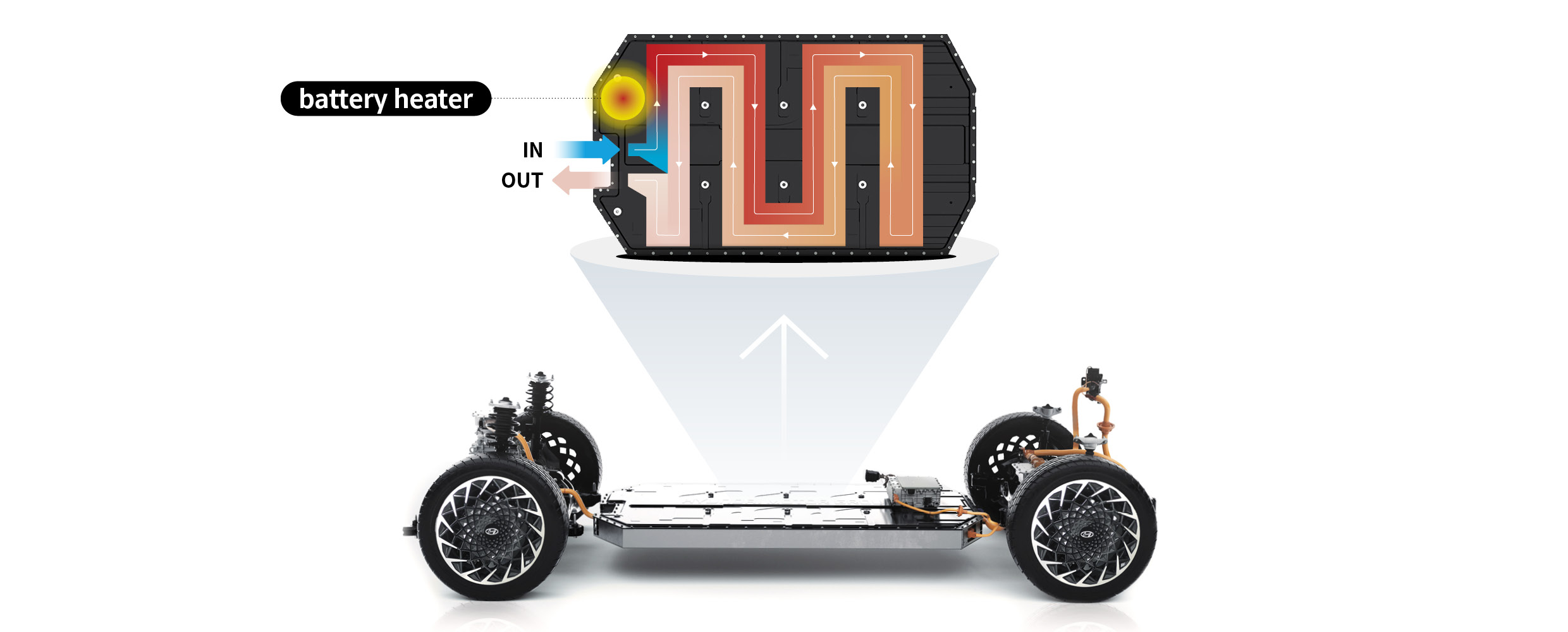
Hyundai Motor Group has adopted a battery heater-type warming technology for its electric vehicle models. The battery pack is structured to have the coolant flowing through it to regulate temperature, which is heated by a battery heater located at the coolant inlet to raise the temperature of the battery. This method uses a heater with high thermal efficiency, consuming less energy.
What’s more, Hyundai Motor Group has refined the charging logic to enable charging in freezing temperatures as low as -30 degrees Celsius. This design prevents the battery from draining while it warms up. In particular, it’s designed so that even if the battery is completely depleted, it’s still possible to charge it by simply attaching a charging cable. This allows the battery to charge as it’s being warmed, allowing the electric vehicle to charge in freezing weather and increasing charging efficiency as well.
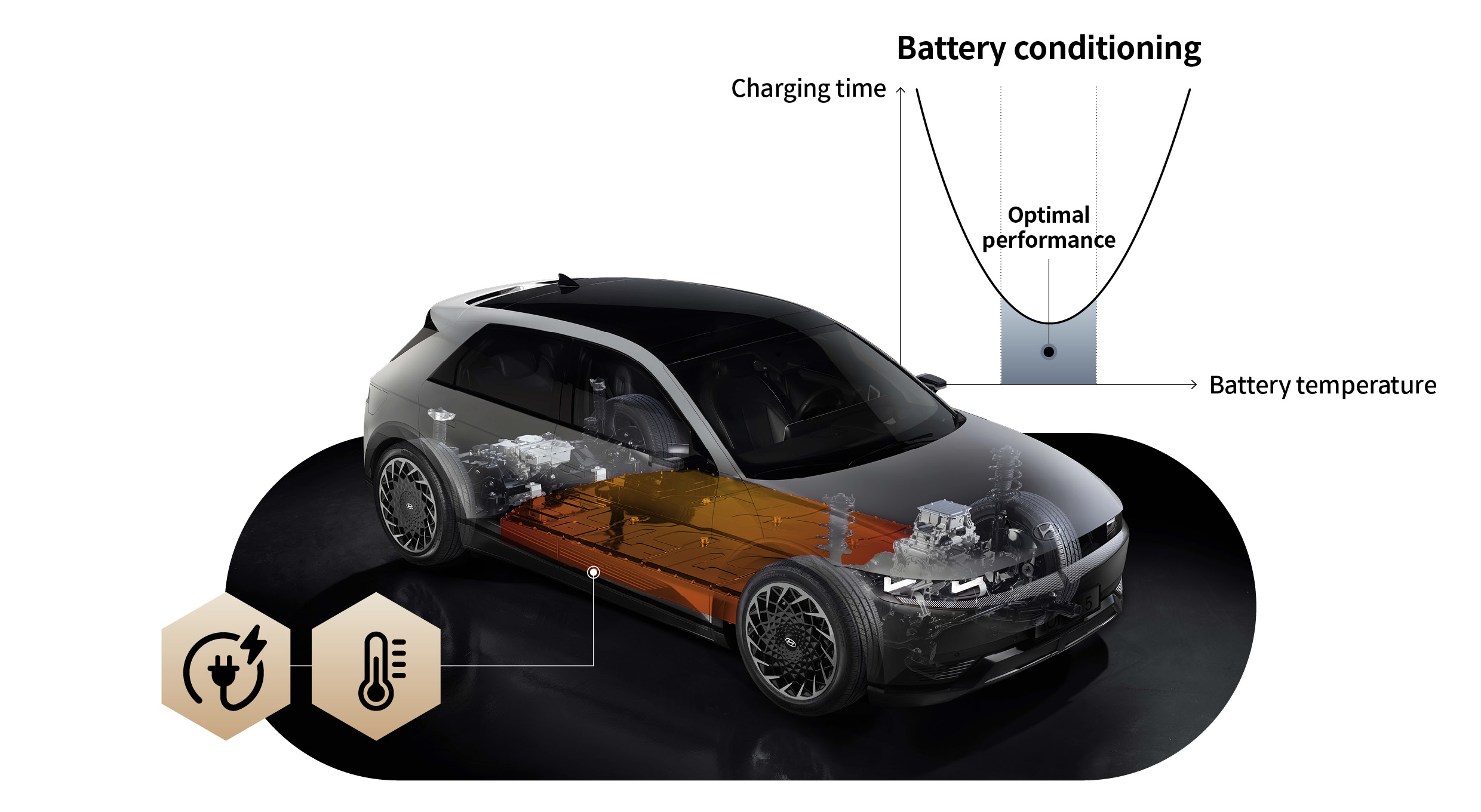
‘Battery conditioning mode’ is Hyundai Motor Group’s representative technology that maintains the performance of electric vehicle batteries in harsh winter conditions. Battery conditioning mode, which is applied to Hyundai Motor Group’s electric vehicles, is an electric vehicle convenience feature that utilizes battery heaters and can be set from the infotainment system. This feature works when you set a rapid-charging station as a waypoint or destination in the navigation and helps control the battery temperature while driving to ensure optimal charging speed.

In terms of driving, battery conditioning mode works primarily in low temperature situations. For example, in conjunction with remote or scheduled air conditioning control during parking, or by optimizing the battery’s power output to improve cold driving performance. The driver can also monitor the battery temperature status in the infotainment system and switch the feature off and on directly. Note that battery conditioning mode operates under different conditions for optimal effectiveness depending on the characteristics of the vehicle model, and the manufacturer recommends setting it to ‘Operating’ to improve charging performance and mileage.

Hyundai Motor Group conducts tests under various chamber conditions when developing its vehicles to ensure optimal performance in various temperature environments that can be encountered in the global market. This includes, of course, testing the performance of electric vehicle batteries in extreme cold conditions. The tests, which take place at the Namyang Research Center’s Environmental Vehicle Development Test Center, check charging performance in extremely cold environments of -30 degrees Celsius or below. Various battery performance tests are also conducted, including optimizing charging time through a thermal management.

Won Woo Suh, Manager of the Electric Driving Test Team 5, in charge of the battery performance tests, explained chamber tests, saying, “We are doing research into the optimal combination for various parameters such as battery charging current and heater capacity and charging efficiency to increase product competitiveness.” In response to a question about changes in the testing environment, Suh answered, “Abnormal weather conditions are becoming more frequent, and we’re facing more diverse environments to respond to. We at Hyundai Motor Group plan to further expand our testing standards to ensure that customers can drive our electric vehicles without any problems, no matter the situation,” expressing the company’s commitment to improvement product competitiveness from a user perspective.
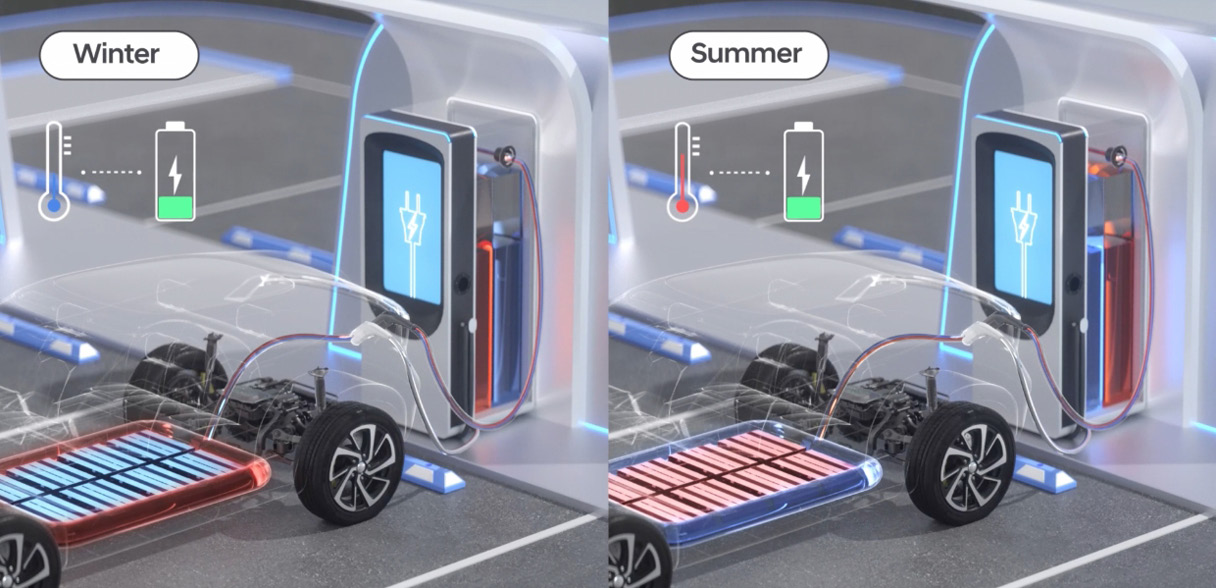
Current electric vehicle thermal management technologies use only the energy of the electric vehicle itself, which inevitably affects mileage. Hyundai Motor Group is devising innovative ways to utilize external energy from charging stations to maximize the energy efficiency of electric vehicles. Simply put, charging stations would be equipped with both hot and cold coolants, and the charging station would directly inject the coolant needed based on the battery temperature.
Such a technology would allow the battery temperature to be controlled to maximize charging speed while preserving the internal battery capacity. While this technology is currently in a conceptual stage, Hyundai Motor Group estimates that it could reduce charging speeds by up to 40% by saving the time it takes to cool or warm the coolant.

Hyundai Motor Group’s electric vehicles can guarantee commercial value even in extreme cold conditions because the company has taken into account the various environments in which their customers drive. This reflects the design philosophy of providing the best possible mobility experience for every customer, every single time. This is why Hyundai Motor Group’s electric vehicles are gaining traction in the global market at a time when many manufacturers are competing in the EV era.