




Last year, Hyundai Engineering & Construction unveiled its ‘Waste-to-Hydrogen Production Package,’ powered by biogas, at ‘H2 MEET 2023,’ the largest hydrogen-focused exhibition in the country. Biogas is a type of bioenergy produced from organic waste, including food scraps, sewage sludge, and livestock manure. Hyundai E&C is pioneering the production of biogas by converting residuals, often blamed as a major source of environmental pollution, into energy for daily use. This article examines the processes and technologies Hyundai E&C utilizes to produce biogas and contribute to resource recycling.
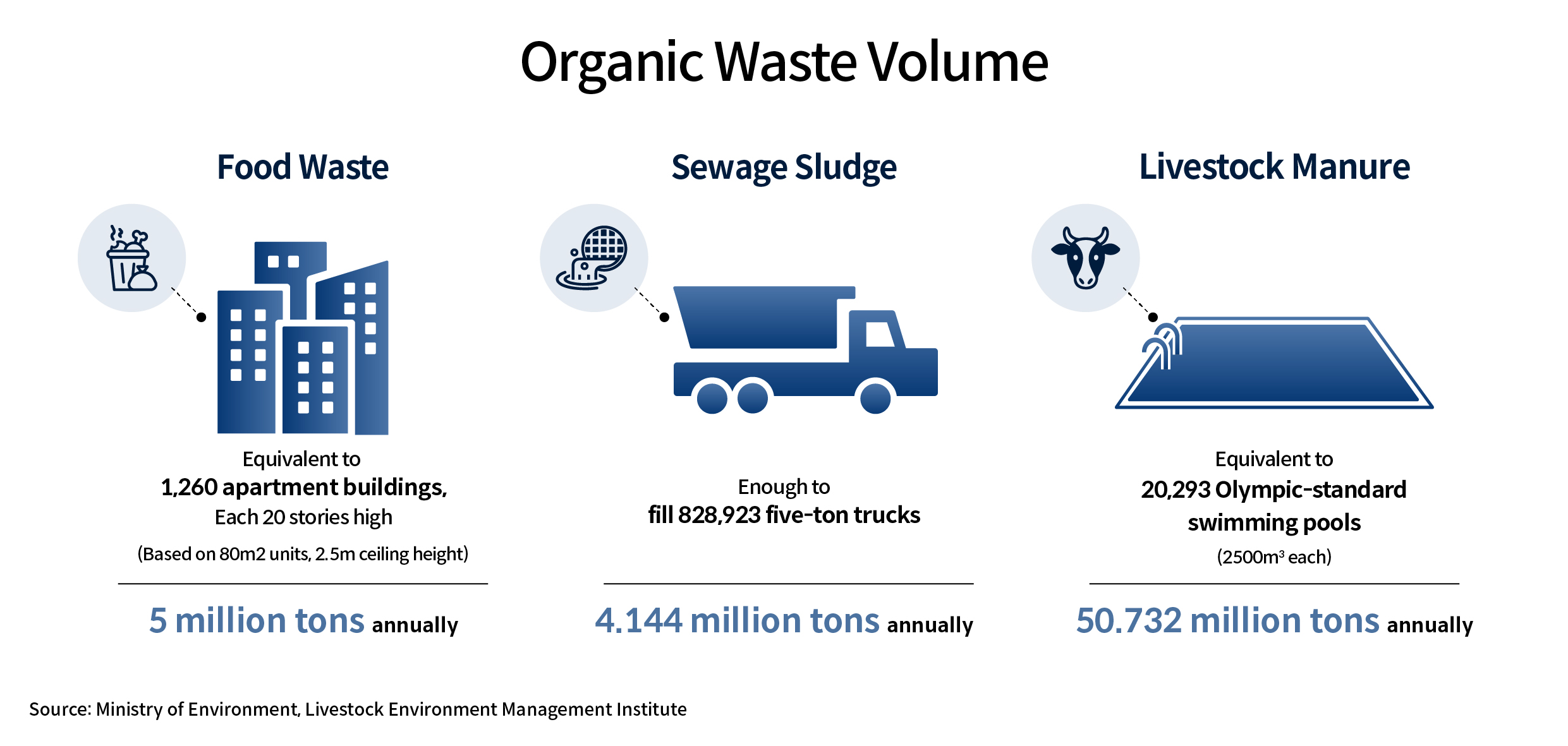
Five million tons of food waste, 4.14 million tons of sewage sludge, and 50.73 million tons of livestock manure: these are the amounts of organic waste generated annually in South Korea as of 2021. A massive volume of organic waste, equivalent to 1,260 twenty-story apartment buildings, around 829,000 five-ton trucks, and 20,293 swimming pools of 2,500m^3 each, poses a global challenge. The significant costs associated with waste management, combined with the need to control greenhouse gases, wastewater, and other byproducts of the disposal process, make it a complex issue.
Biogas is produced by converting waste into a new energy source with substantial added value. Its dual benefits of waste disposal and energy generation are what make this innovation so remarkable. Recognizing the potential of biogas, the government announced the ‘Act on the Promotion of Biogas Production and Utilization Using Organic Waste’ in December 2023. The government anticipates that the implementation of this law will process 5.57 million tons of organic waste annually by 2026, replace 230 billion KRW worth of fossil fuels, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 1 million tons.
The primary components of biogas produced from organic waste are methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). This composition allows biogas to be used for generating electricity and heat or to be upgraded into city gas and clean hydrogen, making it a promising alternative energy solution.
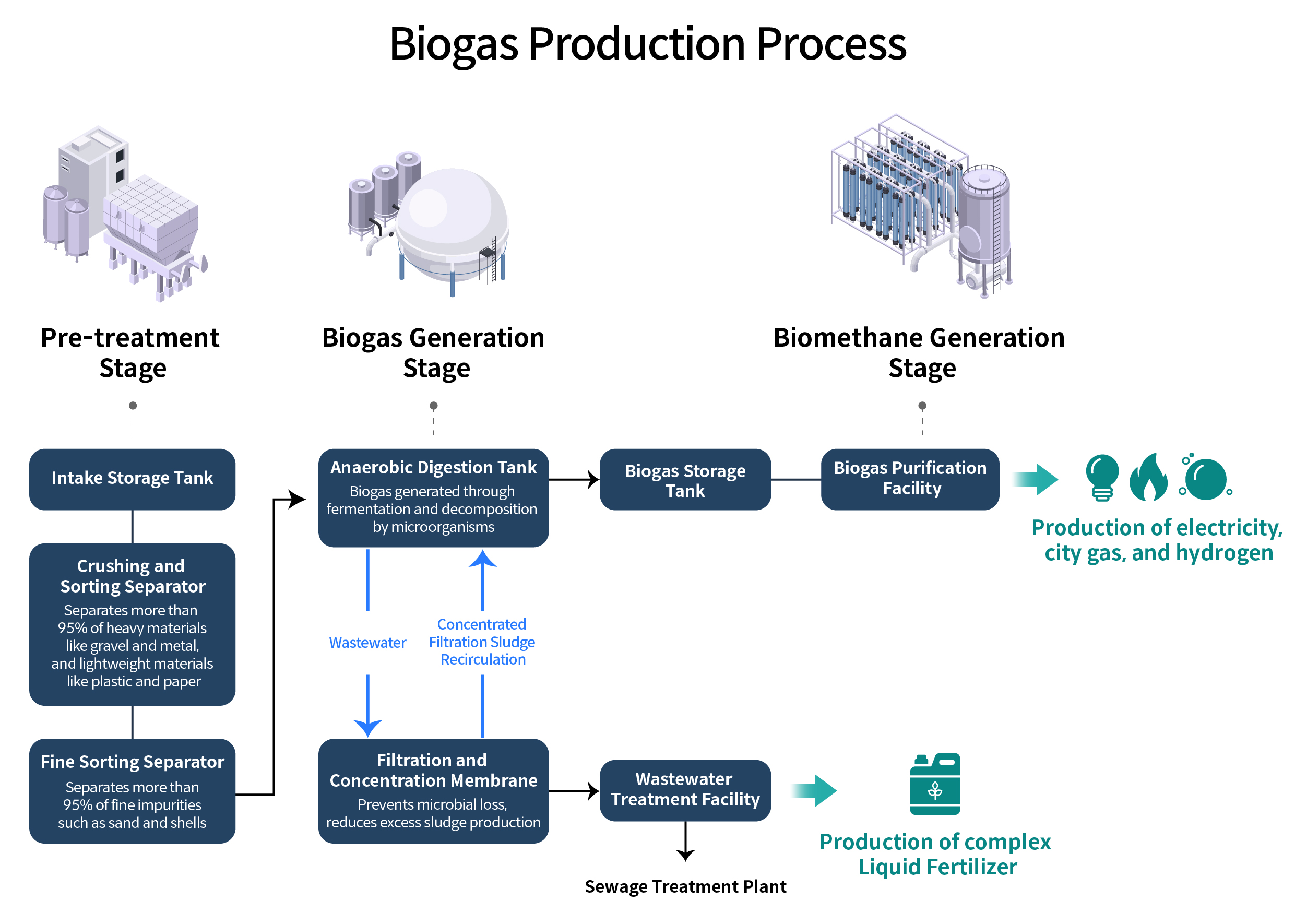
How exactly is biogas produced? The process begins when the collected waste is brought to an intake storage tank at the treatment facility. From there, it undergoes pre-treatment stages such as shredding, sorting, and liquefaction, depending on the type of organic waste. After the pre-treated effluent has gone through these stages, it moves to the anaerobic digestion tank, where it undergoes fermentation and decomposition by microorganisms, resulting in the production of biogas. It is similar to how the human body produces gas, like flatulence, during the digestion of food in the stomach. After biogas is generated, the remaining wastewater passes through a filtration and concentration membrane for recirculation, with a portion of the sludge returned to the anaerobic digestion tank for additional biogas production. The recirculated wastewater is then either discharged to the sewage treatment plant after biological treatment or utilized as a complex liquid fertilizer through a resource recovery process.
The biogas produced in the anaerobic digestion tank is transferred to a storage tank, where it undergoes further purification to become biomethane with a purity exceeding 97%. This biomethane can then be utilized as city gas, vehicle fuel, electricity, or as a precursor for hydrogen production. Moreover, the carbon dioxide remaining after methane is extracted from biogas can be utilized in industrial manufacturing and agriculture.
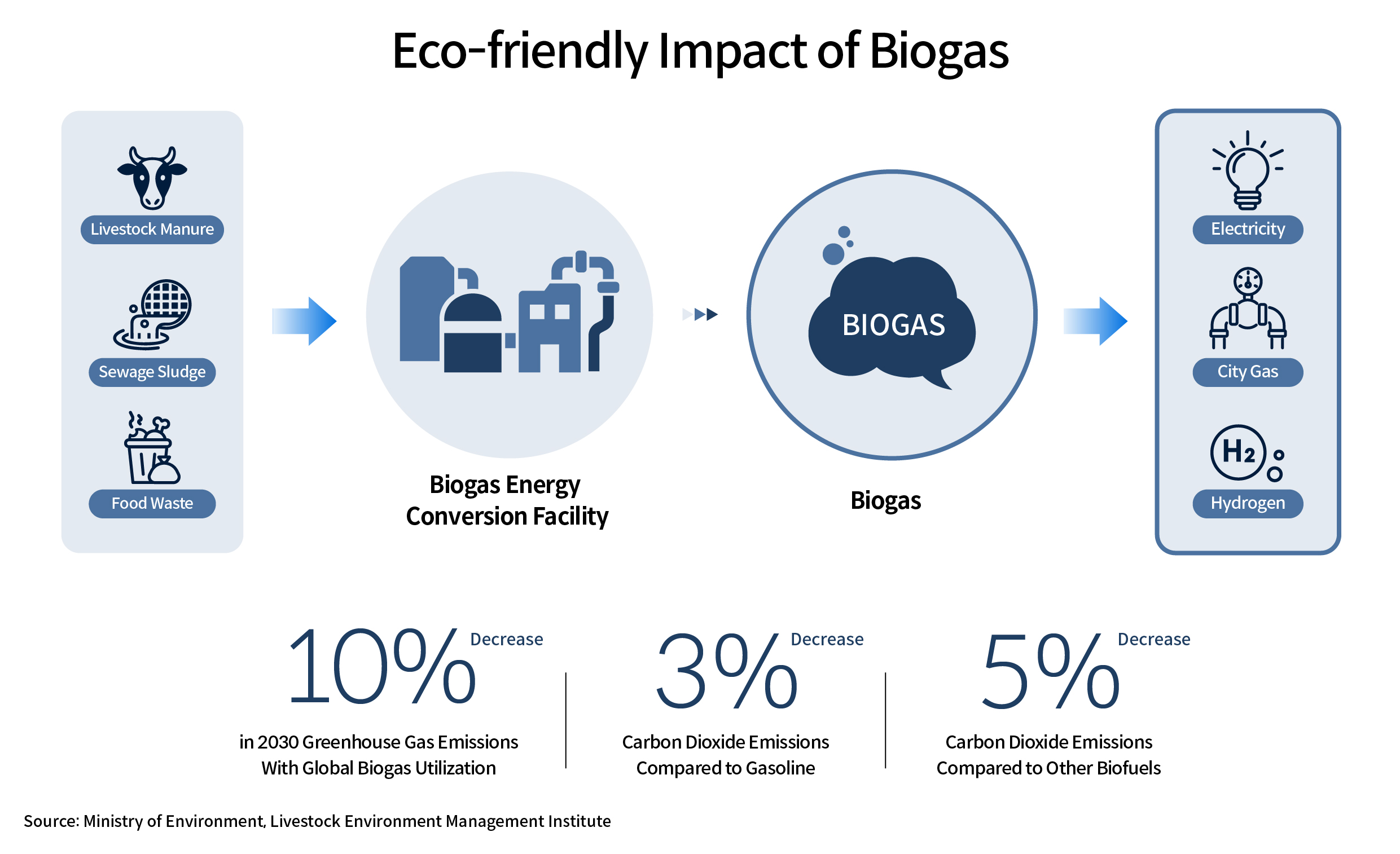
According to a report by the World Biogas Association (WBA), more than 105 billion tons of organic waste are produced globally each year. By converting this waste into biogas, it is possible to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 10% by 2030. Additionally, the carbon dioxide emitted during biogas production is only about 3% of that generated when producing gasoline, and just 5% compared to other biofuels. Since the carbon dioxide produced can be repurposed for other uses, biogas becomes an energy source with nearly zero carbon emissions.
As global efforts to reduce greenhouse gases become increasingly urgent, biogas is gaining recognition as a sustainable and effective solution, with the related market steadily growing at an average annual rate of 9.2%. Hyundai E&C quickly recognized the potential of biogas and focused on acquiring the necessary expertise. This enabled them to develop proprietary solutions, successfully build biogas production facilities, and lead the field of organic waste biogas energy through long-term operation.
Since 2008, Hyundai E&C has ben actively developing biogas-related technologies and has achieved significant results. By establishing a pilot facility in Cheongna, Incheon, for biogas energy conversion, they succeeded in stabilizing biogas production after continuous research and refinement. In 2016, a Food Waste Biogas Energy Center was established in Chungju, Chungcheongbuk-do. This facility, which operates using entirely domestic technology, can process an average of 80 tons of food waste per day to produce biogas.
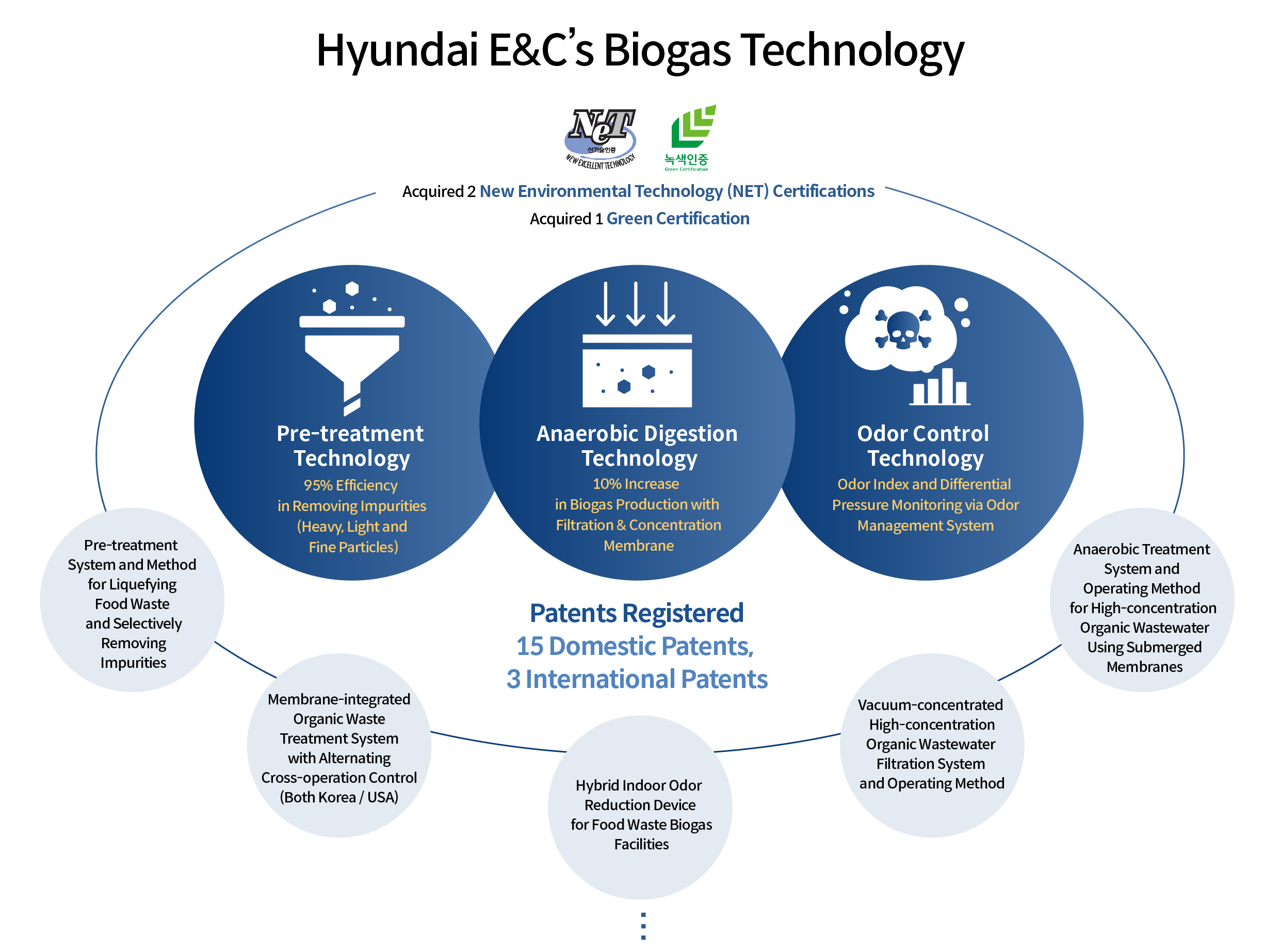
The successful operation of the Cungju Food Waste Biogas Energy Center is due to Hyundai E&C’s long-term efforts in localizing and refining related technologies. Conventional biogas production technologies that relied on foreign expertise did not fully align with the characteristics of locally produced waste, leading to a reduction in biogas production efficiency. To address this issue, Hyundai E&C applied its proprietary technology, specifically developed to suit the domestic environment, in biogas production. Hyundai’s biogas-related technologies encompass three key areas: food waste pre-treatment, anaerobic digestion, and odor control, all of which have been tailored to better suit local waste conditions.
Food waste pre-treatment requires a more delicate process than the pre-treatment of livestock manure or sewage sludge. Hyundai E&C’s advanced technology can filter out up to 95% of fine contaminants, exceeding the capabilities of conventional methods. Korean food waste often has a thick consistency, making it difficult to filter out fine impurities using conventional equipment. Unfiltered contaminants can lead to issued such as pump malfunctions, pipe blockages, and sedimentation in digestion tanks. In response, Hyundai E&C developed pre-treatment technology and equipment tailored to local food waste, effectively separating and removing fine contaminants to enhance digestion efficiency.
Anaerobic digestion is the central technology in the production of biogas. Biogas is generated from pre-treated effluent. Hyundai E&C enhanced biogas production efficiency by incorporating a recirculation step. This process extends the retention time of sludge, prevents microorganism loss, and removes more than 80% of volatile solids. Additionally, the increased retention time of both sludge and microorganisms results in a more than 10% increase in biogas production compared to existing facilities. The process of treating organic waste and generating biogas often produces unpleasant odors. Previously, these odors were released into the atmosphere, potentially impacting the surrounding environment. Hyundai E&C addressed this issue by developing Korea’s first real-time odor concentration management system, effectively resolving the problem. The system features a sealed closed-circuit design to prevent odor spread and employs odor collection technology tailored to the specific characteristics of each section of the production facility. The captured odors are purified through a deodorizer before being released in a significantly cleaner state. With this technology, Hyundai E&C aims to achieve maximum efficiency and optimal environmental conditions throughout the entire biogas production process. The excellence of their technology has been demonstrated through achievements such as securing two New Environmental Technology (NET) Certifications, one Green Certification, and 18 domestic and international patents.
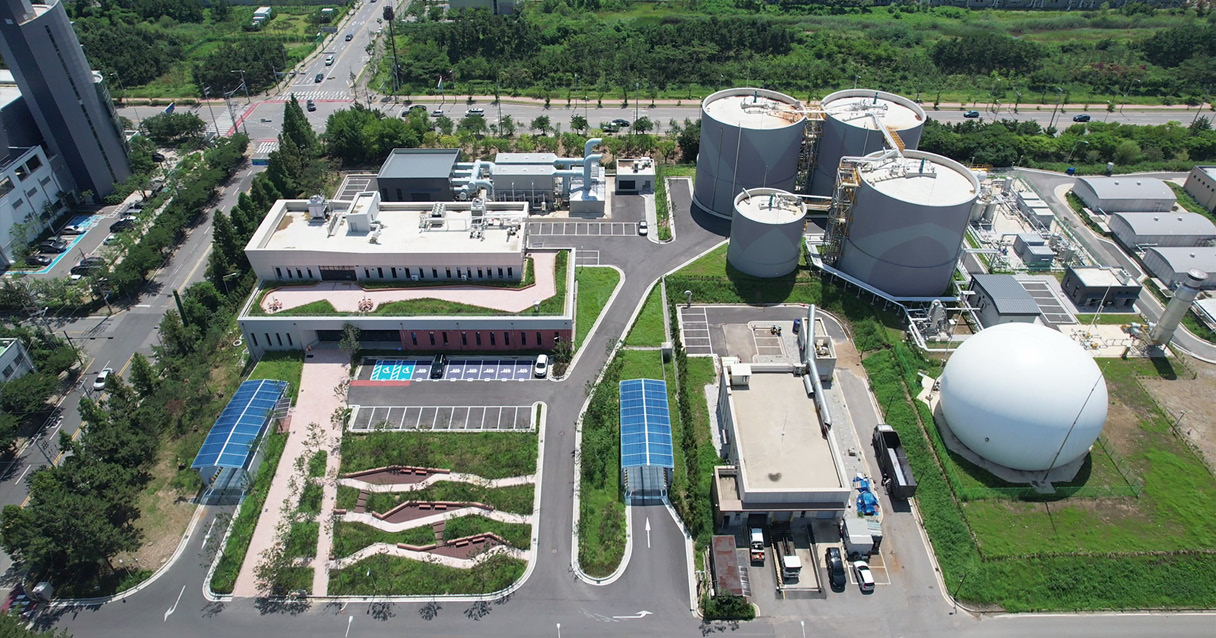

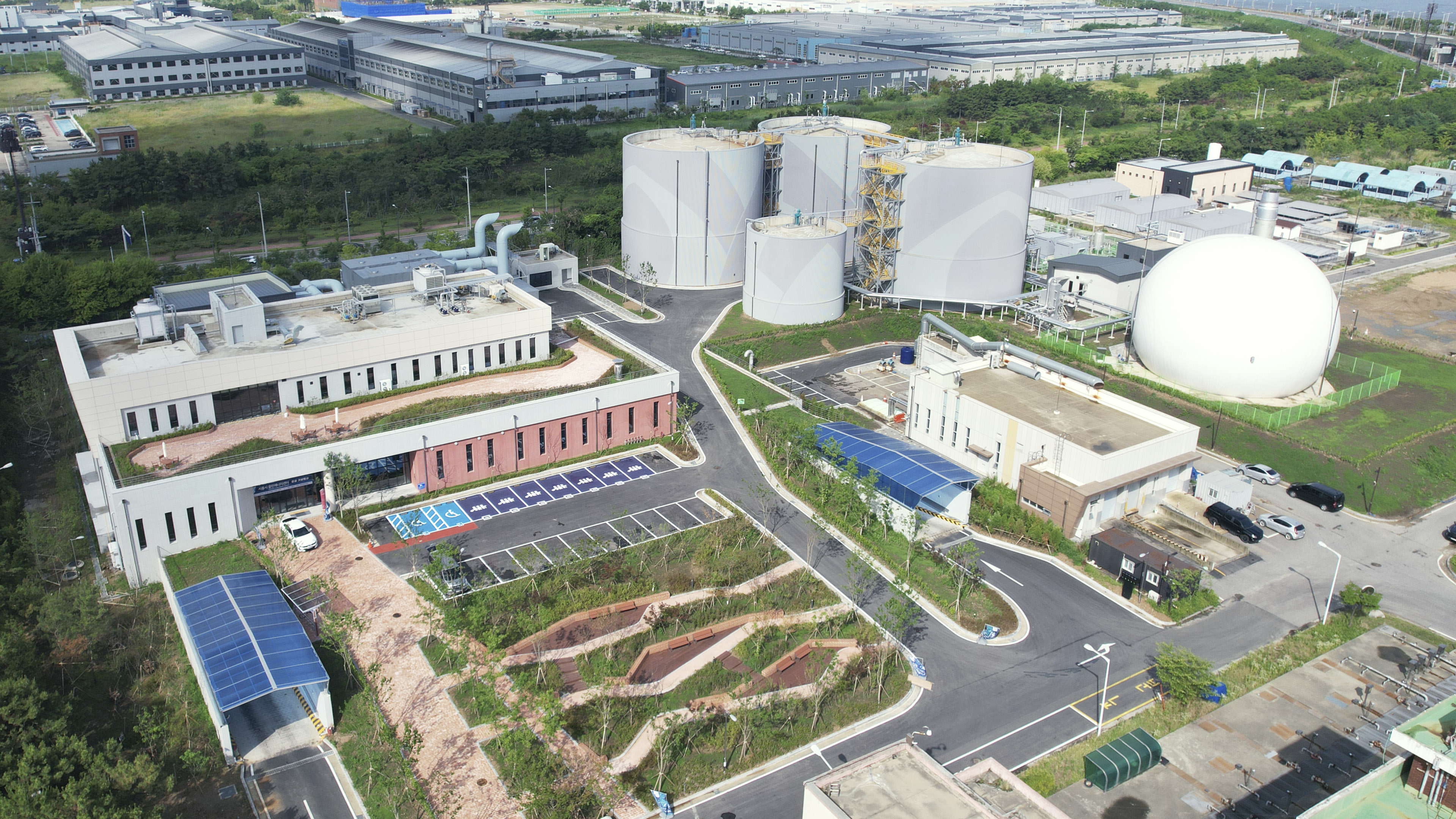
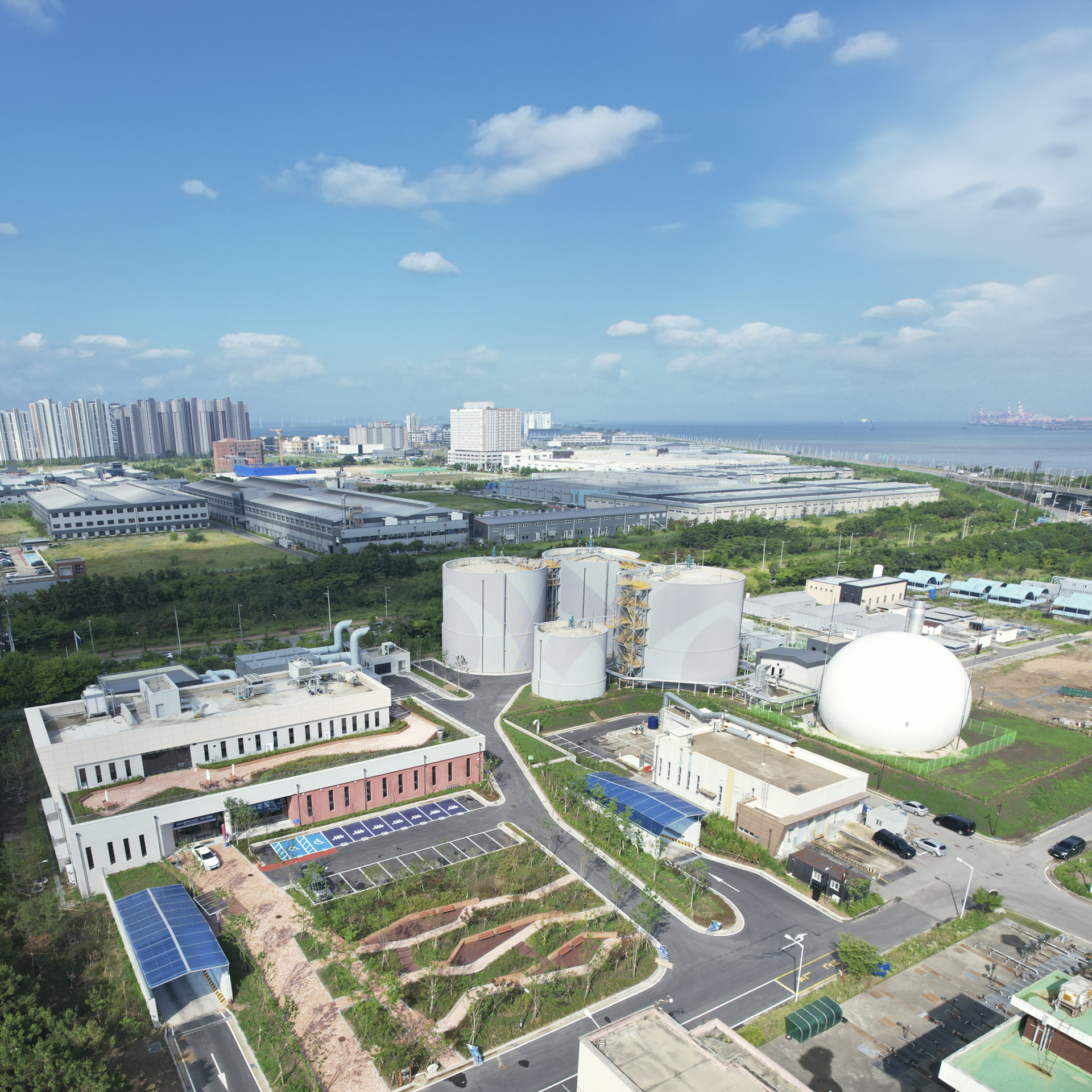
Hyundai E&C is leveraging the expertise and proven technology acquired from establishing and operating the Chungju Bioenergy Center to drive business expansion. On July 3rd, the Siheung Clean Energy Center commenced operations as Korea’s first privately-funded integrated biogas facility, showcasing Hyundai E&C’s cutting-edge biogas technology. This center, an integrated waste treatment facility, spans 33,430 square meters within the Siheung Water Environment Center in Gyeonggi-do Province.
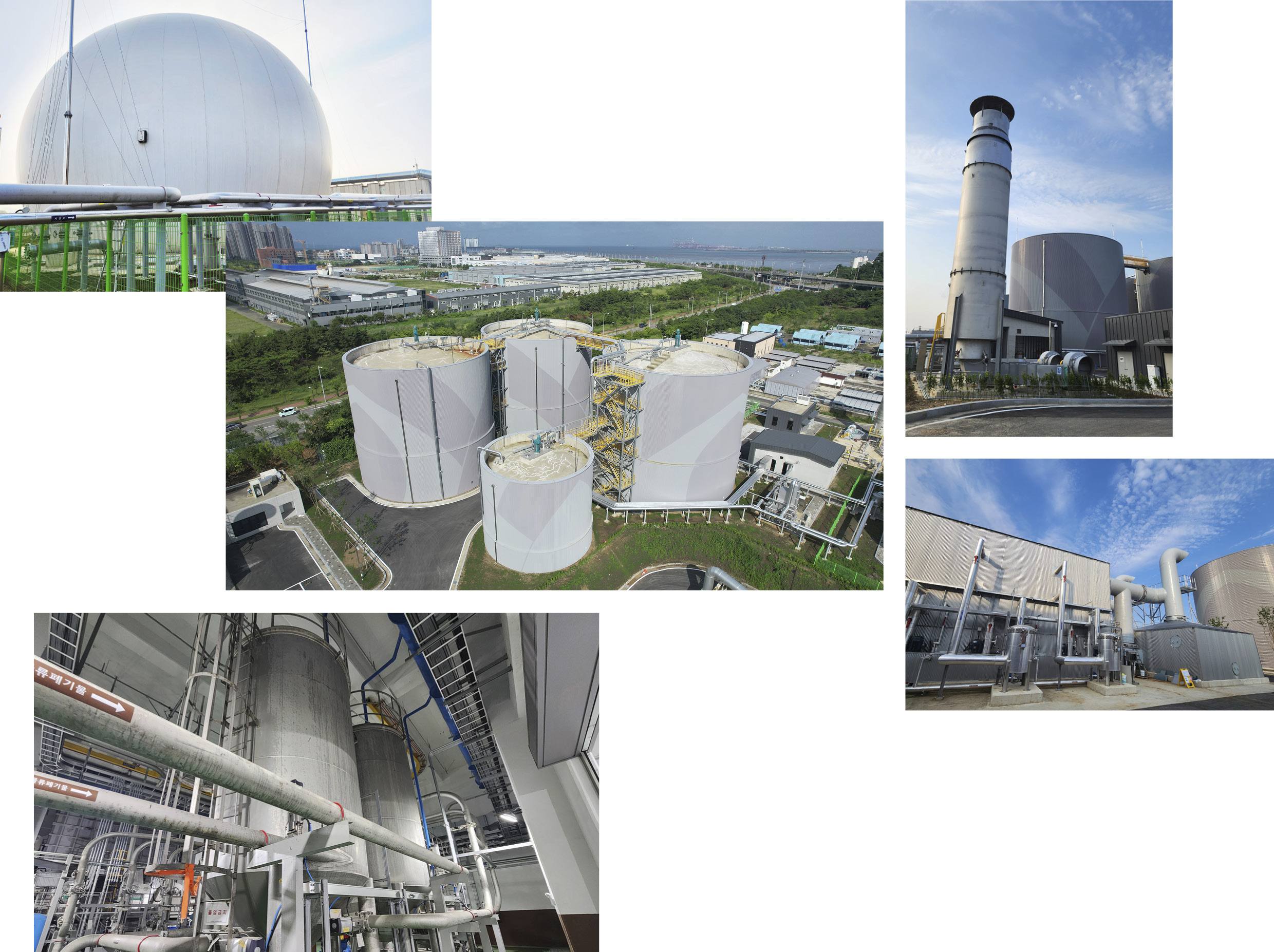

The facility comprises various systems, including pre-treatment, anaerobic digestion, thermal hydrolysis, sludge processing, wastewater treatment, and odor removal. It handles the large volumes of waste generated daily in Siheung – 145 tons of food waste, 540 tons of sewage sludge, and 60 tons of manure – and produces approximately 4.6 million Nm³ of city gas annually thorough biogas upgrading. The city gas produced here is enough to supply about 8,282 households daily and is distributed throughout the entire Siheung area. The Siheung Clean Energy Center is praised for addressing both ‘local environmental improvement’ and ‘energy supply’ by effectively managing the increased organic waste resulting from regional development and population growth.
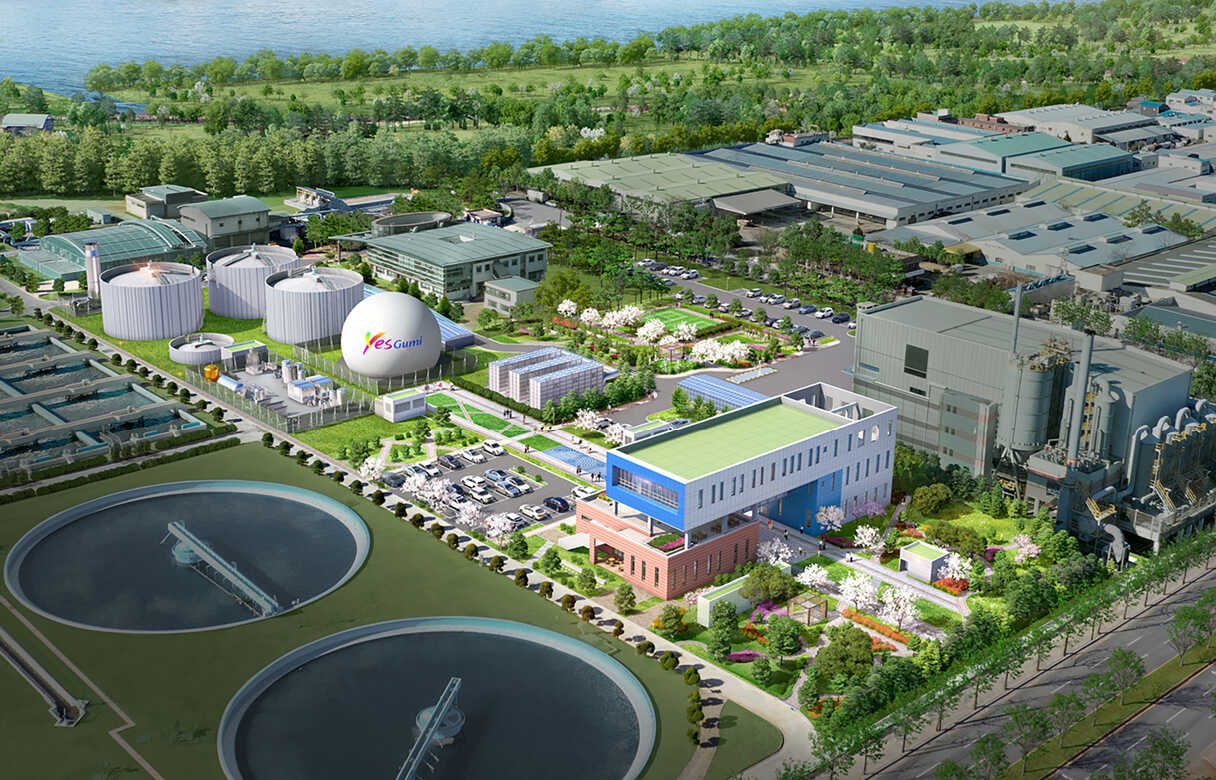

Having taken a meaningful first step in establishing the energy industry ecosystem, Hyundai E&C is now preparing for the next phrase. As part of a national project awarded by the Ministry of Environment in April 2022, Hyundai E&C is set to build an integrated biogas energy demonstration facility. The facility is scheduled for completion in 2026 and will be capable of processing up to 75 tons of organic waste per day. It will incorporate advanced technologies, including improved pre-treatment processes and self-sufficient energy generation for its operations.
Additionally, Hyundai E&C has been selected as the preferred bidder for the Gumi Metropolitan Integrated Biogas Facility private investment project. The plan is to generate biogas from 475 tons of organic waste produced in Gumi and Chilgok area, supplying it as city gas. This project is expected to produce 5.5 million Nm³ of biogas annually, sufficient to supply city gas to 9,000 households.

We can no longer pursue indiscriminate energy production for the sake of human convenience. It is crucial for everyone to consider how to protect the planet while meeting our energy needs. The value of biogas lies in its ability to manage organic waste, a major source of odors and greenhouse gases, while also playing a pivotal role in resource circulation. Hyundai E&C recognized the potential of biogas early on and has been at the forefront of the biogas energy industry’s growth by consistently developing proprietary technologies. This commitment will lay the foundation for a resource-circulating society and contribute to creating a cleaner planet for the future.