




Hyundai Motor Group’s first smart urban mobility hub, Hyundai Motor Group Innovation Center Singapore (HMGICS), completed its automation process by incorporating artificial intelligence (AI), which was introduced in Pt. III previously. Information generated during the operation of the production center is collected, selected, and accumulated into data, and this data becomes the basis for making optimal decisions in each area. Previously, we learned about the core technologies and systems at HMGICS, which operates the data-focused facility.
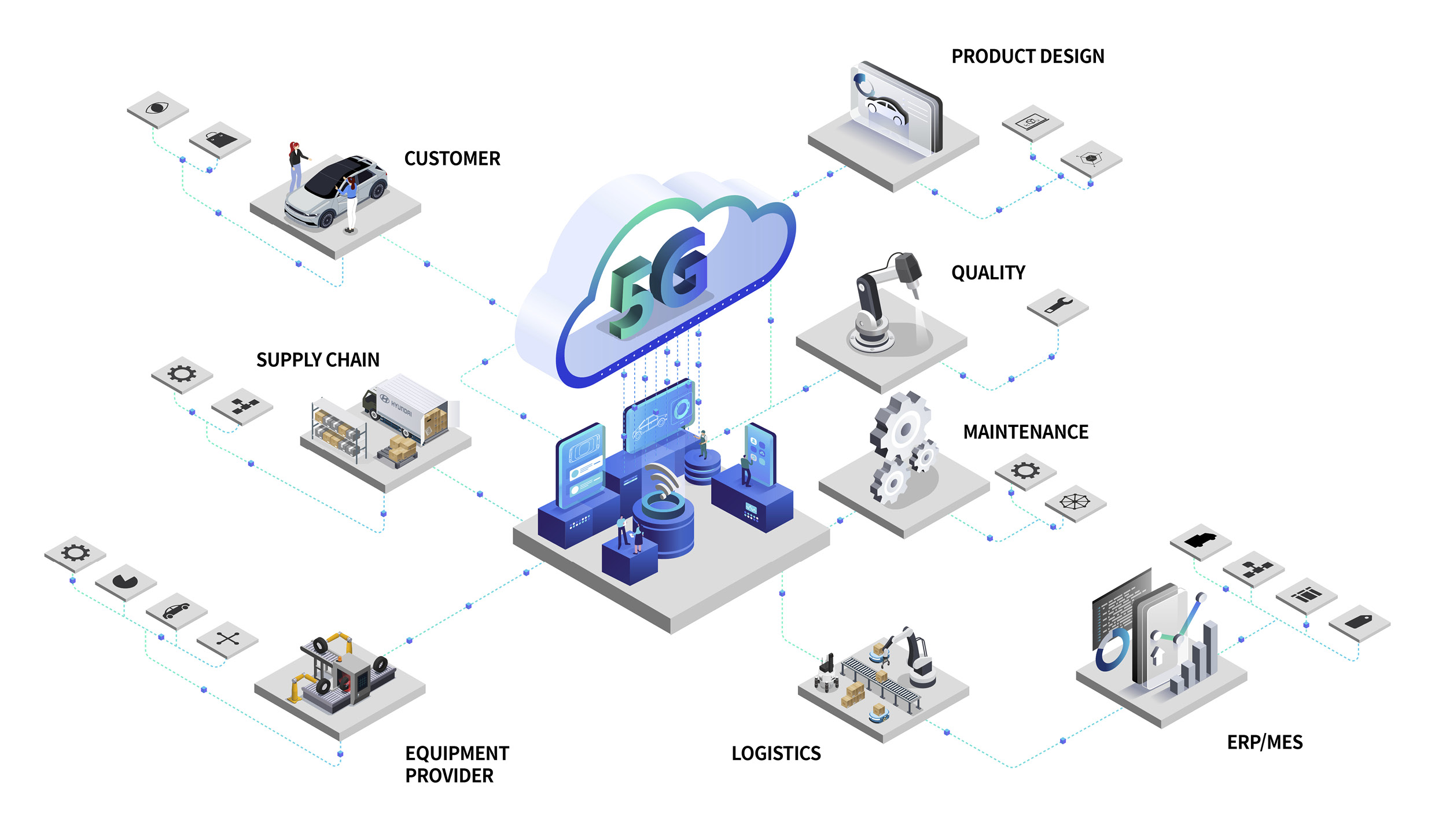
A conventional automotive factory, composed of many different processes, produces hundreds or thousands of cars per day. During this process, a lot of data ends up being generated. For example, it’s possible to obtain simple numerical information — such as the number of doors a robot assembles per day, or how long it takes to do so — but it’s also possible to learn why specific processes are prone to frequent errors. This data can be used to indicate ways to optimize the factory’s operations.
However, unlike the latest factories that have embraced digital technology, factories of the past have not been able to capitalize on this data. It was difficult to build the infrastructure to collect and analyze data generated during the production process, and the information accumulated by workers could not be used as meaningful data because it remained only as know-how belonging to the individual.

It’s clear why today’s manufacturing companies are pursuing a transformation towards smart production powered by digital technologies. This is because saving and sharing data generated from every process can help reduce wastage, contribute towards optimizing methods, and increase production efficiency. By analyzing data, it is possible to reduce the cost and time required for production, minimize unplanned risks such as human error, and ultimately improve the quality of products.
In this way, smart production facilities are fueled by data. Therefore, to operate a manufacturing center like HMGICS, the infrastructure to collect, select, and utilize data must be in place. This means that a ‘digital transformation’ is necessary, which involves converting all production facilities to digital entities so that information generated during the production process can be accumulated as data.
However, digitizing existing processes and facilities requires a significant amount of time and money. For example, to attach sensors to identify abnormal parts, or record the movement of a machine, new equipment must be introduced or the process must be stopped. It’s also not easy to integrate a data system that is already being used with new facilities. This is why it is difficult to convert existing factories to centers of digital excellence, like HMGICS. So, what process did Hyundai Motor Group plan to smoothly collect and use HMGICS data?
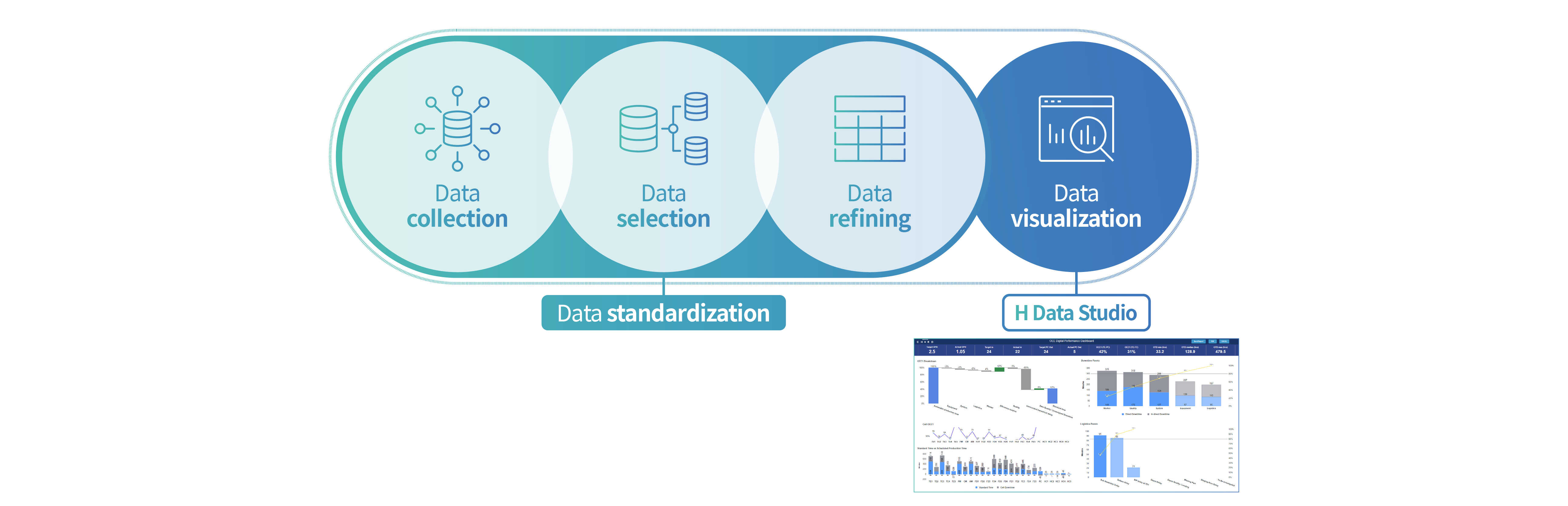
To develop the HMGICS smart urban mobility hub, Hyundai Motor Group began by processing data from each area into one type. Raw data generated from various processes cannot be used as is. Information generated from each area, such as planning, logistics, and production, must be processed to enable smooth sharing.
The production process at HMGICS generates a large amount of data, as machines produce different car models in automated cells and robots move freely between these cells. HMGICS performs a selection process to pick out the required data from this large amount of information.
This selected data is refined further. This refers to the labeling process, filtering out irrelevant data and collecting and sorting necessary data only. Data has different names and formats, such as images, audio files, and sensor data, depending on the area in which it is generated. Therefore, selected data must be adjusted so that they are not interpreted differently and their exact meaning can be understood. This work, called ‘Data Standardization’, is the process of unifying the languages and characters exchanged for smooth communication.
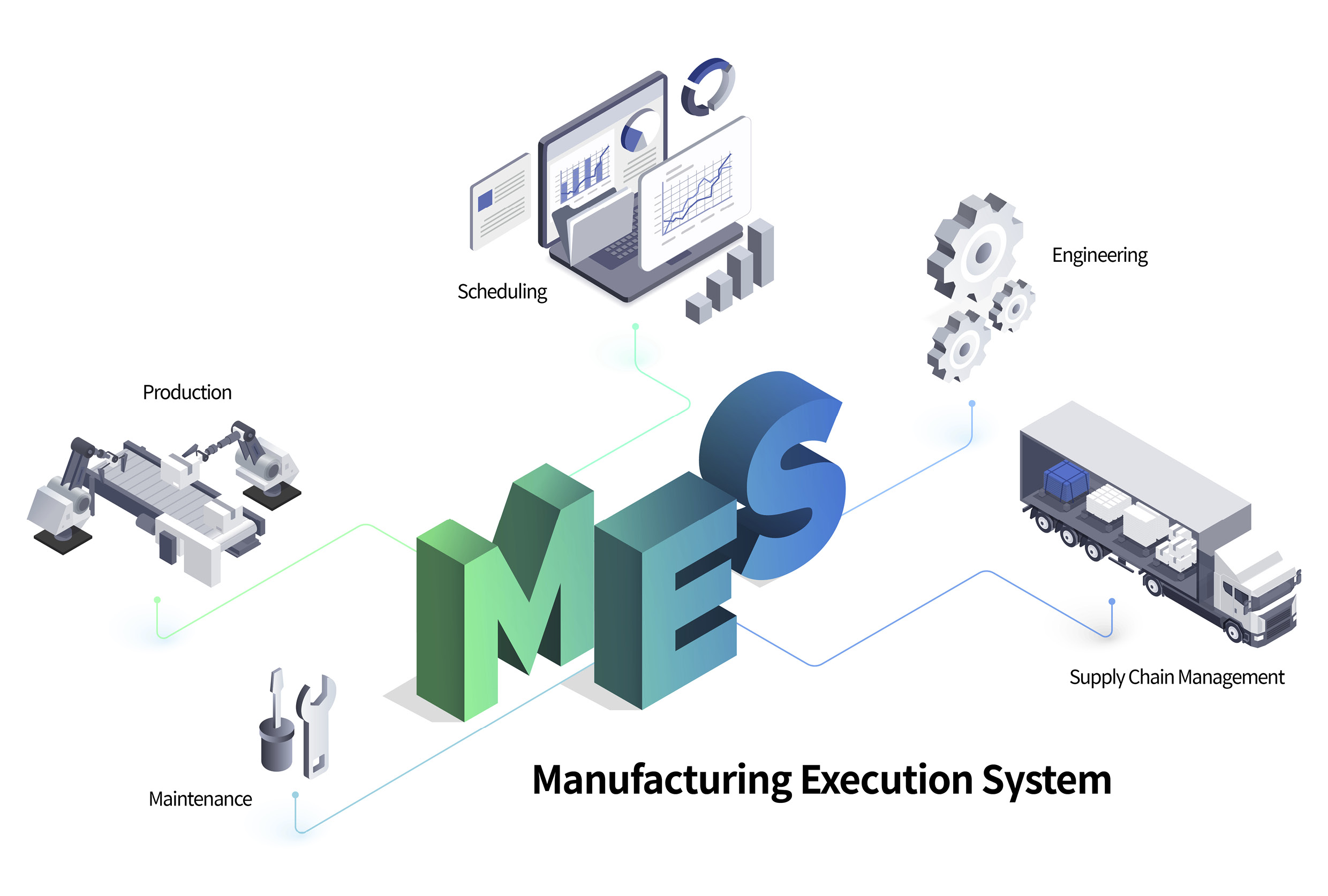
Hyundai Motor Group has developed technology that automatically collects, selects, and standardizes the data that is constantly generated at HMGICS. We have built an integrated platform that can manage and connect data more efficiently.
The “Manufacturing Execution System” (MES) is a platform that integrates and manages standardized data. MES manages the entire HMGICS, ensuring different areas of the factory run smoothly and efficiently. For example, it analyzes historical data to set production targets based on demand, and plans for future production based on current inventory and production needs.
It then directs the work of each cell according to the production plan and oversees the process until each vehicle is finished. MES also orders necessary parts in advance, and if there are any unexpected problems in the process, it revises its plans based on real-time field data. Basically, MES is the key concept in the data-based automation processes.

Like a dashboard that clearly displays a car’s driving speed or status of operation, HMGICS has a “dashboard” that collects data generated from the process and visualizes it so that it can be viewed at a glance.
The “H-Data Studio,” uses software that integrates data from all areas within the factory then displays it on a dashboard. From the dashboard it is possible to get a complete picture of HMGICS’ operations. Also, it contains Data Flow Management (DFM) which shows the data flow between the system and device, to help understanding the overall status of HMGICS. Furthermore, it is highly intuitive and customizable based on the features the user needs.
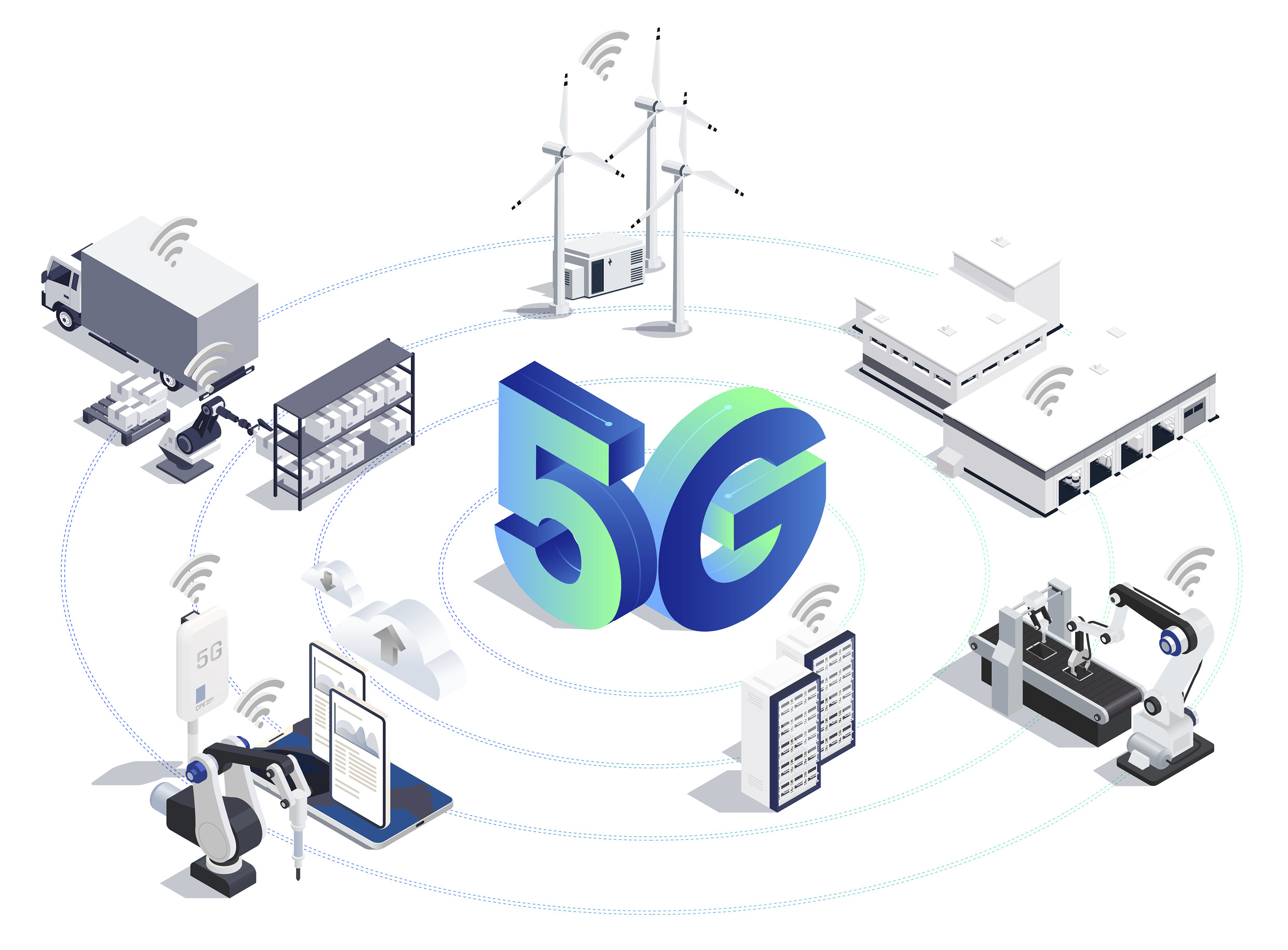
A solid network infrastructure that serves as the basis for smooth data collection and use is also a representative feature of HMGICS. The Innovation Center has built a 5G network to share large volumes of data at high speeds and allow mobile robots to set paths and navigate autonomously. This 5G network implemented throughout the building provides seamless and stable performance, creating a communication system that allows the robots and electronic equipment to work together more smoothly based on the Internet of Things (IoT).
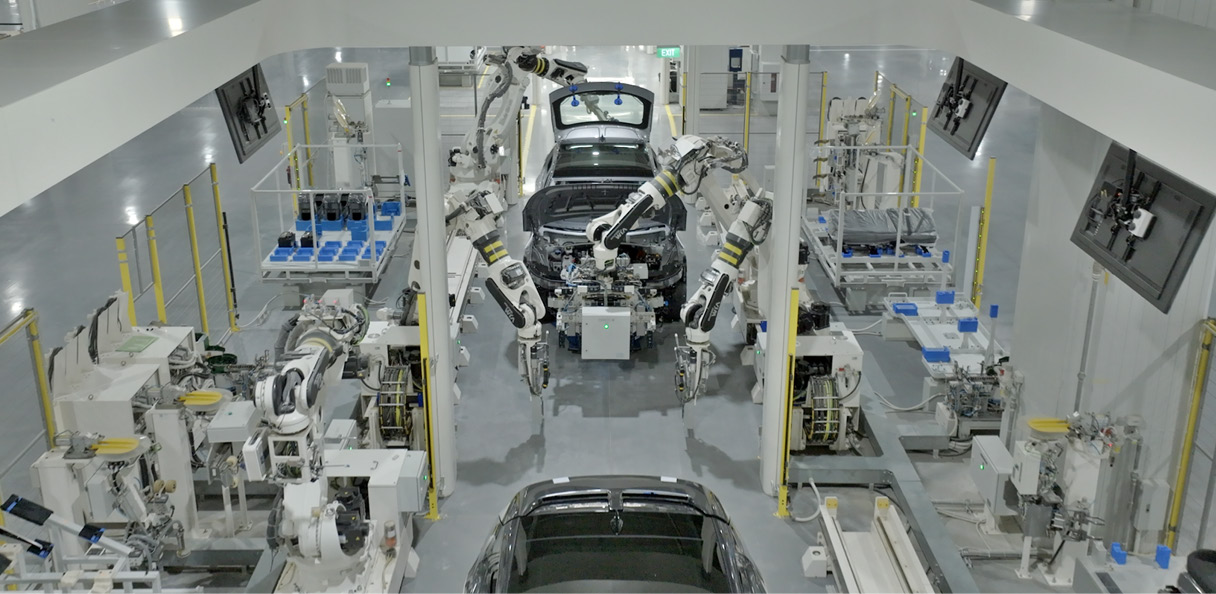

Data is constantly accumulated. Data is accumulating right now. Collection of ‘big data’ enables HMGICS to make faster and more accurate decisions. Hyundai Motor Group plans to expand data obtained from HMGICS to other factories in the future. Ultimately, the group plans to make every factory a smart factory and build a data-driven production facility that operates automatically using only data.
In the final part of this series, we will take a look at robotics technology, another key element that drives HMGICS.
The Full HMGICS Innovation Series
Part 1. The mobility factory without conveyor belts
Part 2. A twin factory in a virtual digital space
Part 3. AI technology — the brain of an intelligent factory
Part 5. Synchronization between people and robots