




The Hyundai Motor Group Innovation Center Singapore (HMGICS) is a manufacturing testbed that organically connects various software-based technologies. Among the various areas of operation and development being researched at HMGICS, “robotics” is one of the representative technologies of the smart factory. Robotics takes over the role of conventional conveyor belts and collaborates with workers to increase production efficiency. In this part, we discover how advanced robotics technologies are utilized at HMGICS.

Today, we can see robots not only in automotive factories, but in a variety of industrial sites, too. This is because robots have become a necessity across almost all industries. Robots can perform tasks that are too dangerous for humans, as well as move quickly and repeatedly to increase production efficiency.
However, it takes a lot of effort and resources to get robots to perform more advanced tasks and expand their scope of use. This is because for each process, the appropriate robot must be selected for the task and working conditions and a program must be designed to accurately control the robot’s movements. Implementing an environment like this ultimately comes down to sophisticated robotics technology.
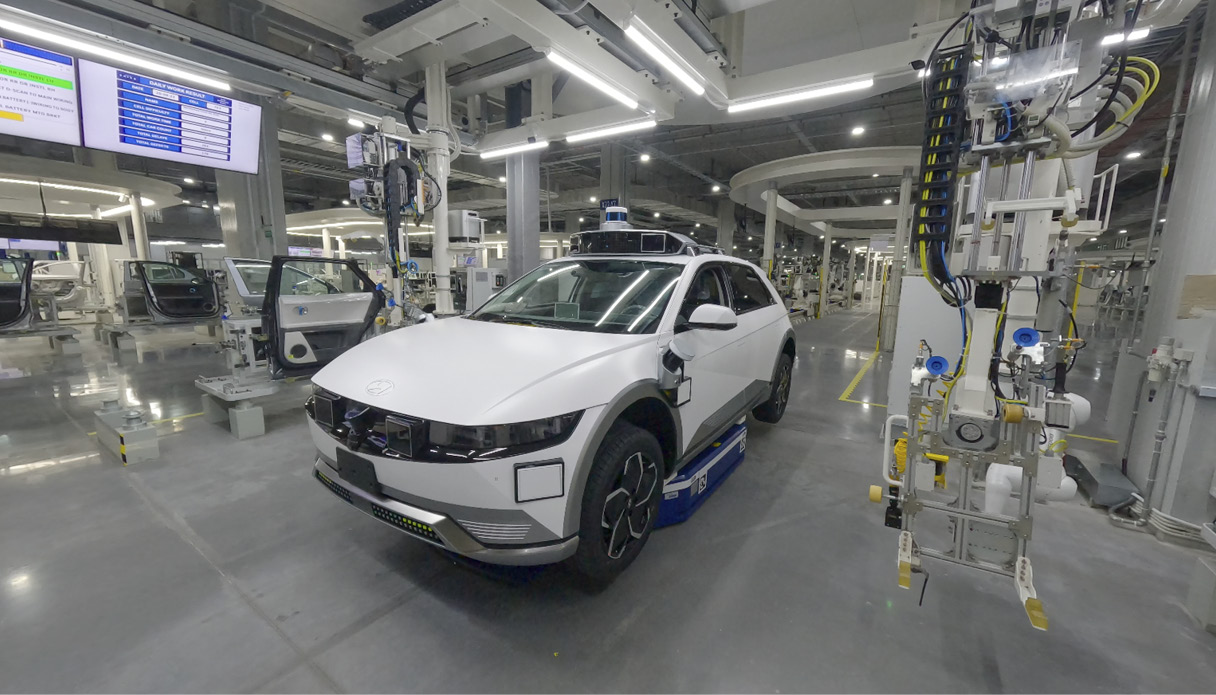

Robotics technology is utilized heavily at HMGICS and the production site is filled with numerous robots moving around busily. Robots of all shapes and sizes bridge the gaps between the series of processes; there are robots that move heavy car bodies in and out of the production cells, robots that carry parts from the warehouses, and robots that pick-up car parts, accurately and precisely assembling them at various work sites. This is a window into the future of mobility production.
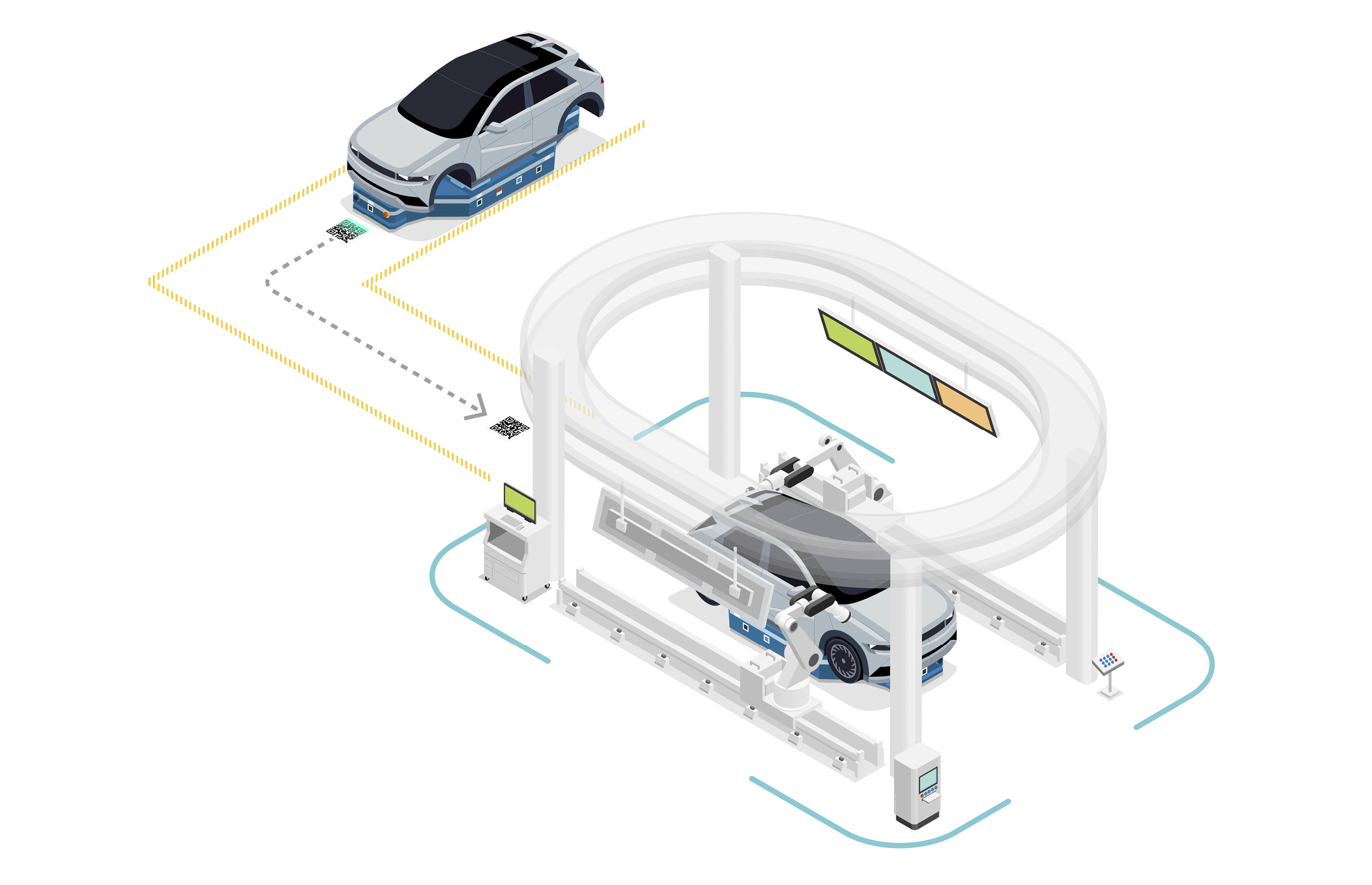
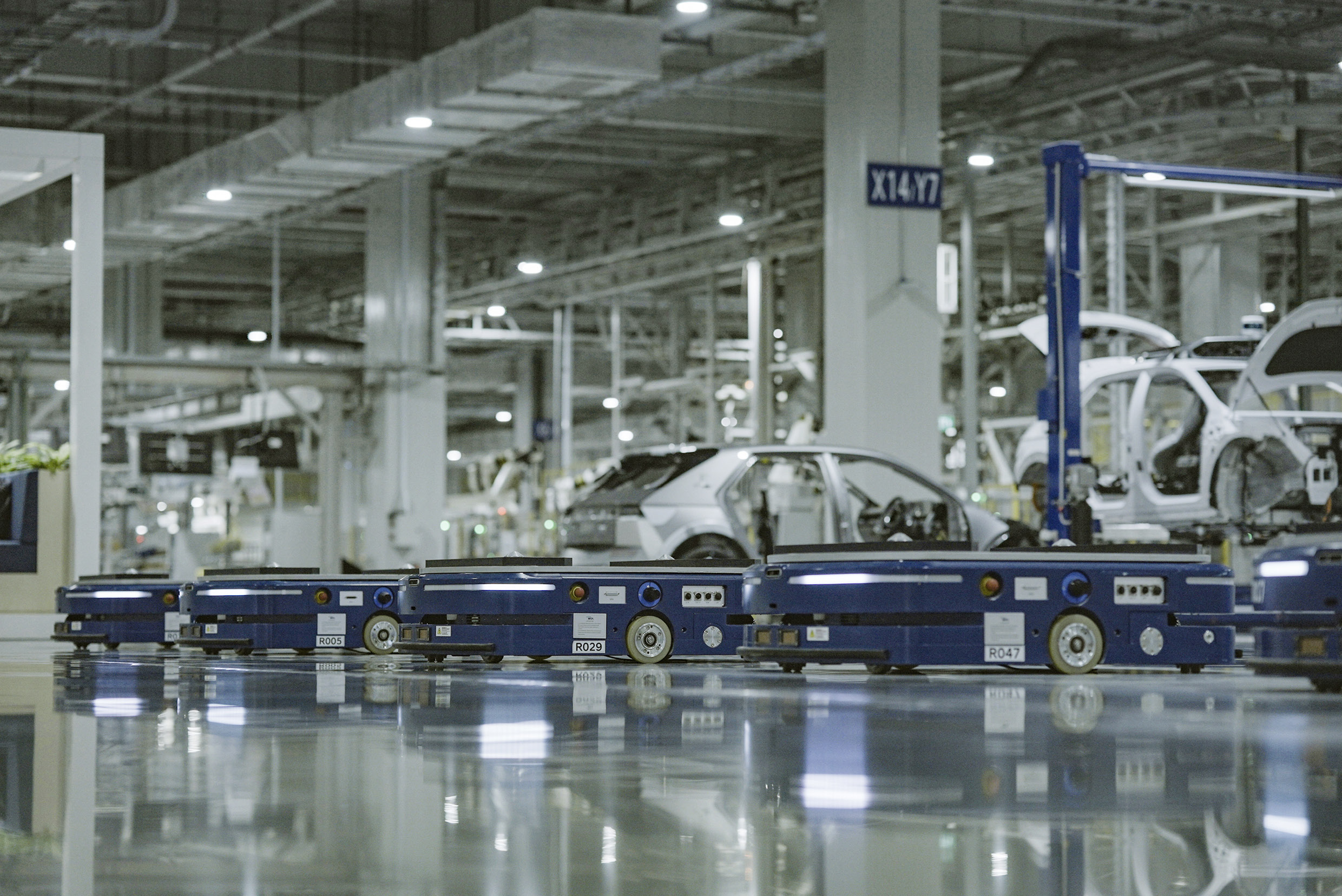
The first robots you’ll notice at the HMGICS production center are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs). AGVs are industrial robots that move autonomously without an operator, and at HMGICS they are responsible for transporting car bodies. In conventional automotive factories, the car body is placed on a conveyor belt that moves in one direction, and cars are produced in a fixed sequence along this line.
However, at HMGICS, where multiple car models can be produced at the same time and without constraints, different processes are performed independently in each cell. Therefore, the car bodies must be moved to each cell according to the work process determined at each moment. The AGVs are responsible for quickly and accurately moving the car bodies into the relevant production cell. In other words, these AGVs take over the role of conveyor belts in a conventional factory. Thanks to the free mobility of AGVs, mixed production is possible using the cell-based production method.
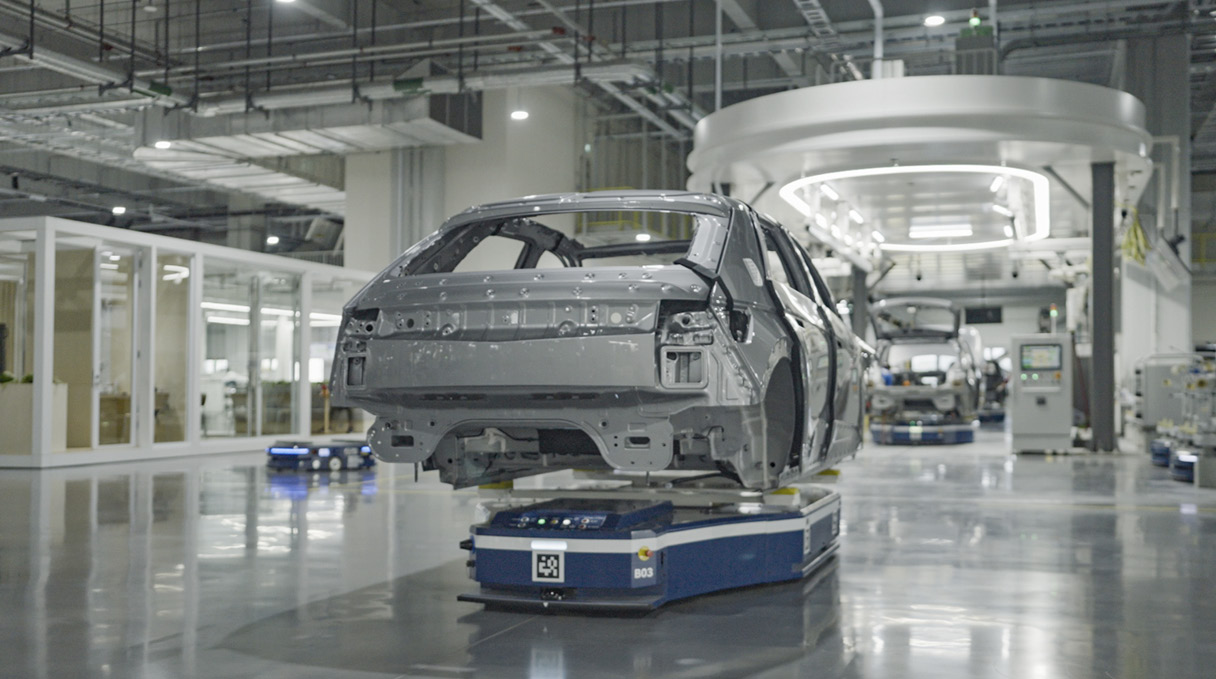

QR codes on the production center floor at HMGICS are scanned by AGVs. These direct the AGVs to their destinations along a designated route. If a robot encounters a person or an obstacle on the way, its safety sensors recognize an obstruction and the robot stops. These are controlled precisely through a mobile robot integrated control system.
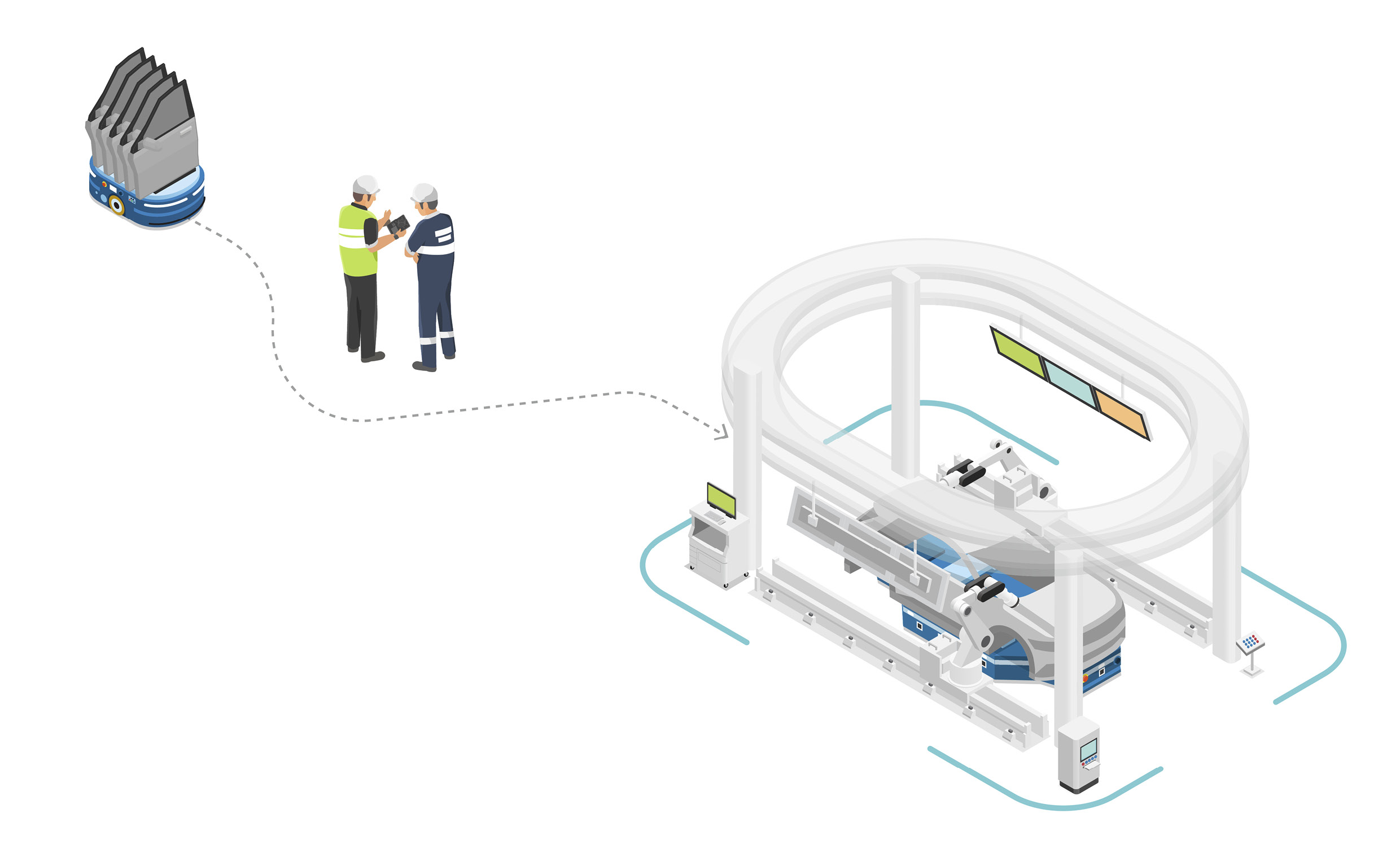
While the AGVs are responsible for transporting the car bodies, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are responsible for transporting parts needed to produce cars. AMRs closely support the cell-based production process, moving the necessary parts from cell to cell. What distinguishes the AMRs from AGVs is that they are equipped with sophisticated LiDAR sensors.
AMRs can recognize the environment and objects around them and navigate the production site autonomously. Once a starting point and destination is programmed, the optimal route will be created — and if an AMR encounters an issue along the way, it will find an alternative route without any external manual input.

Because all AMRs are linked to the robot integrated control system, they never collide with other AMRs. In fact, they automatically navigate and change their routes to avoid collisions. They are much like cars at an intersection with lots of traffic controlled by traffic signals to keep them moving in order. Thanks to the AMRs’ smart navigation system, workers can focus on more creative tasks in the production process.

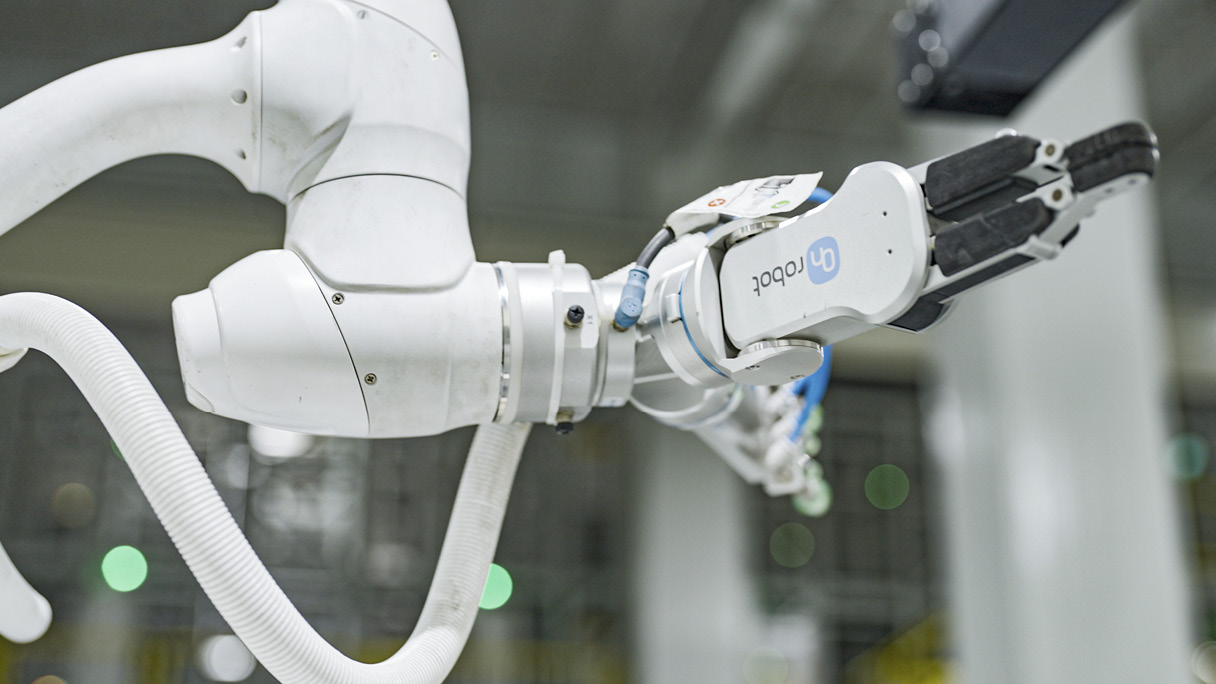
To apply cellular production to the production site, Hyundai Motor Group assigned a number of robots to replace conveyor belts. These robots help implement automated tasks, and complete more sophisticated and efficient processes.
Typically, in automated cells, there are production robots that lift heavy parts, such as roof panels and doors, and assemble them precisely. These robots can mount different parts without problems in a multi-vehicle production system. It’s also worth noting that these collaborative robots automatically adjust a car’s wheel alignment or headlamp irradiation angle and inspect the quality of the car’s assembly. These robots improve the quality of vehicle construction by inspecting components and the result of production processes more accurately than the human eye can.
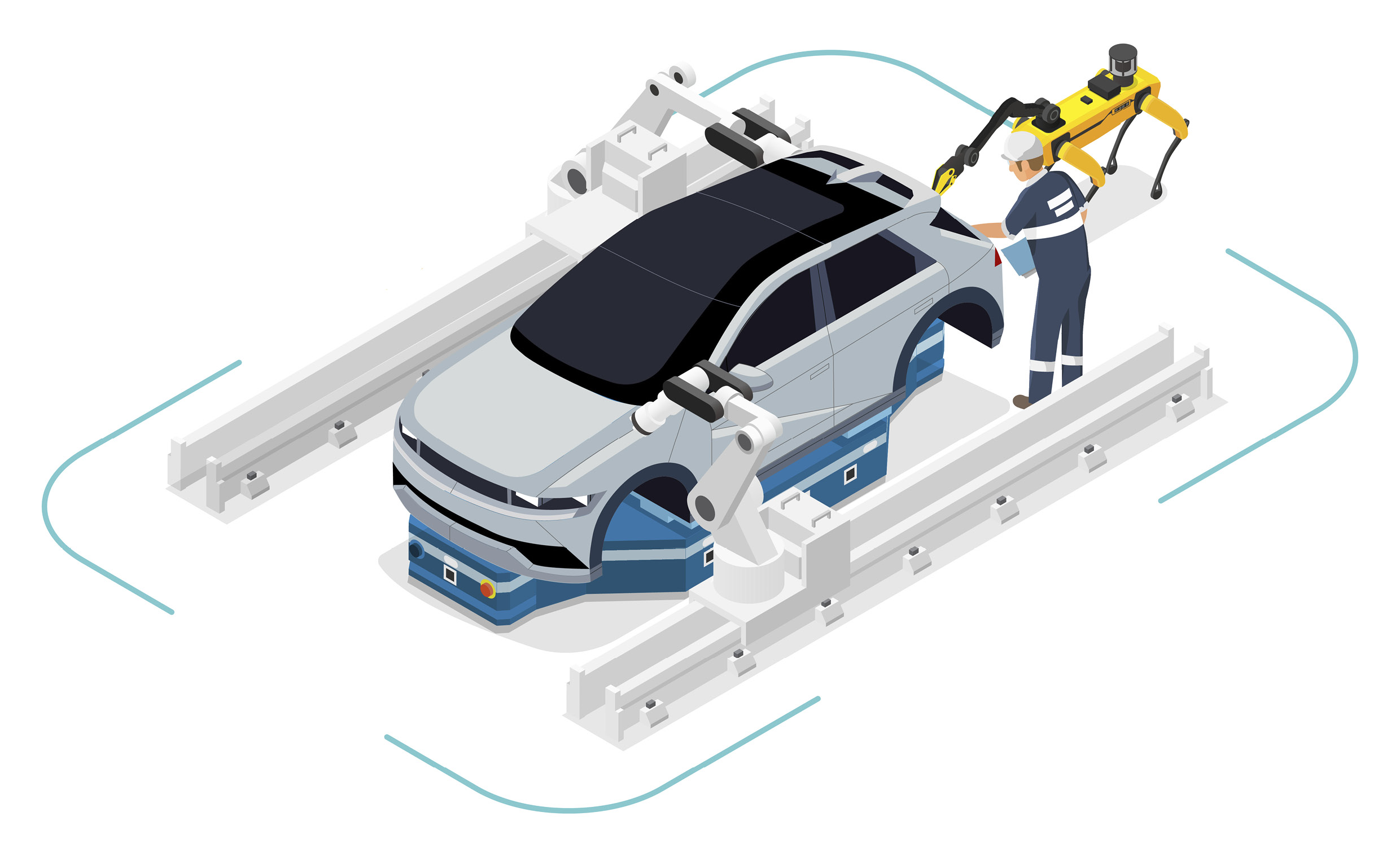
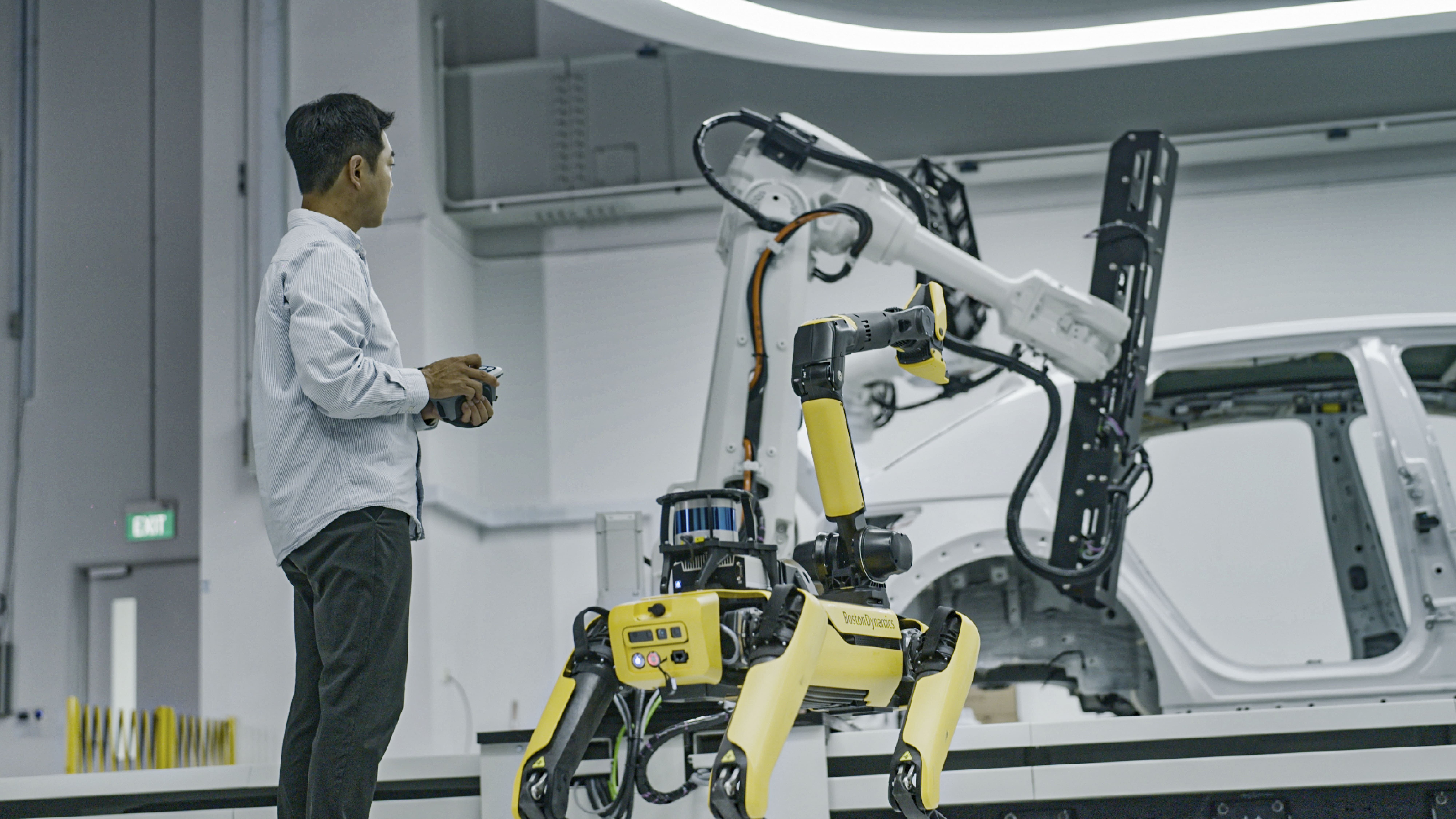
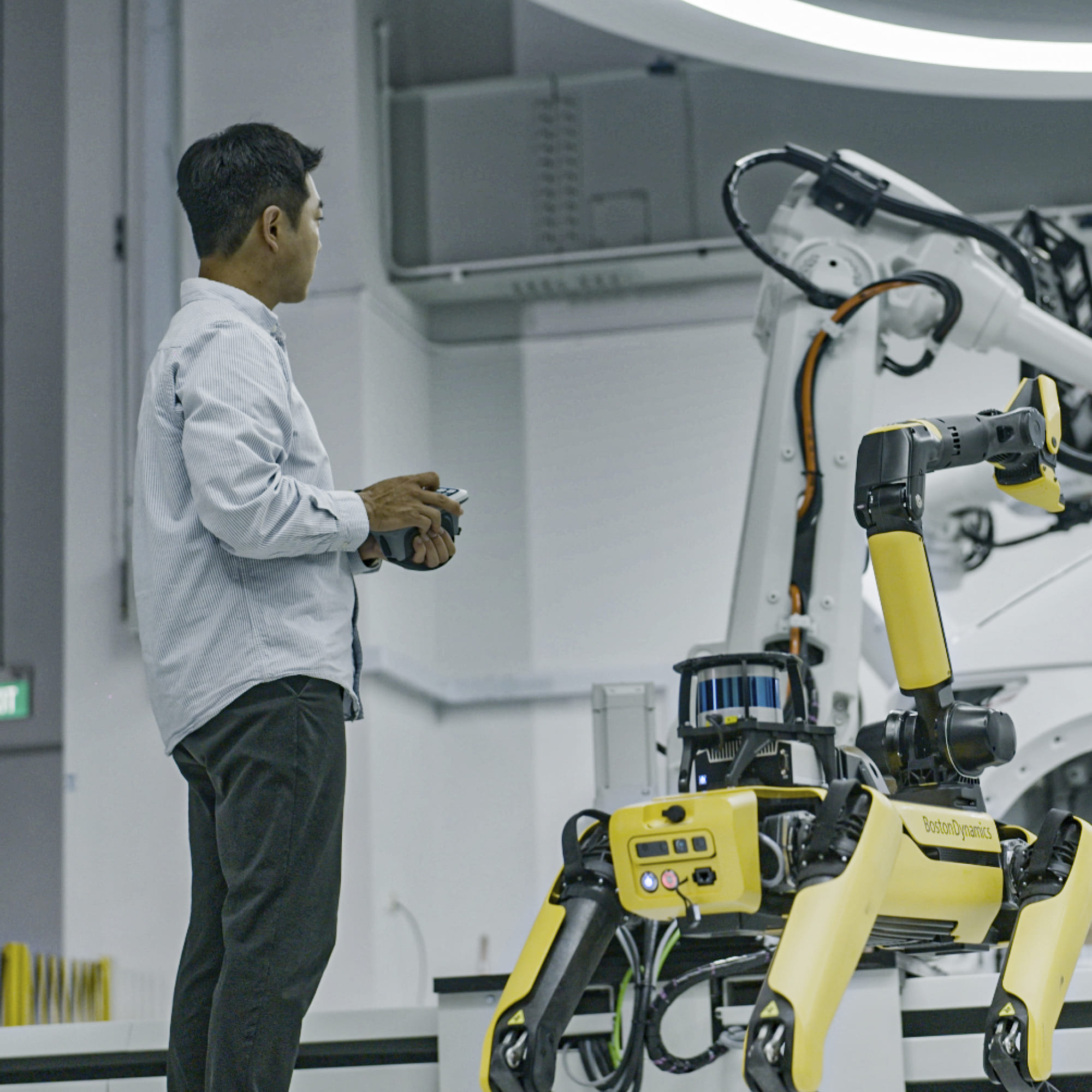
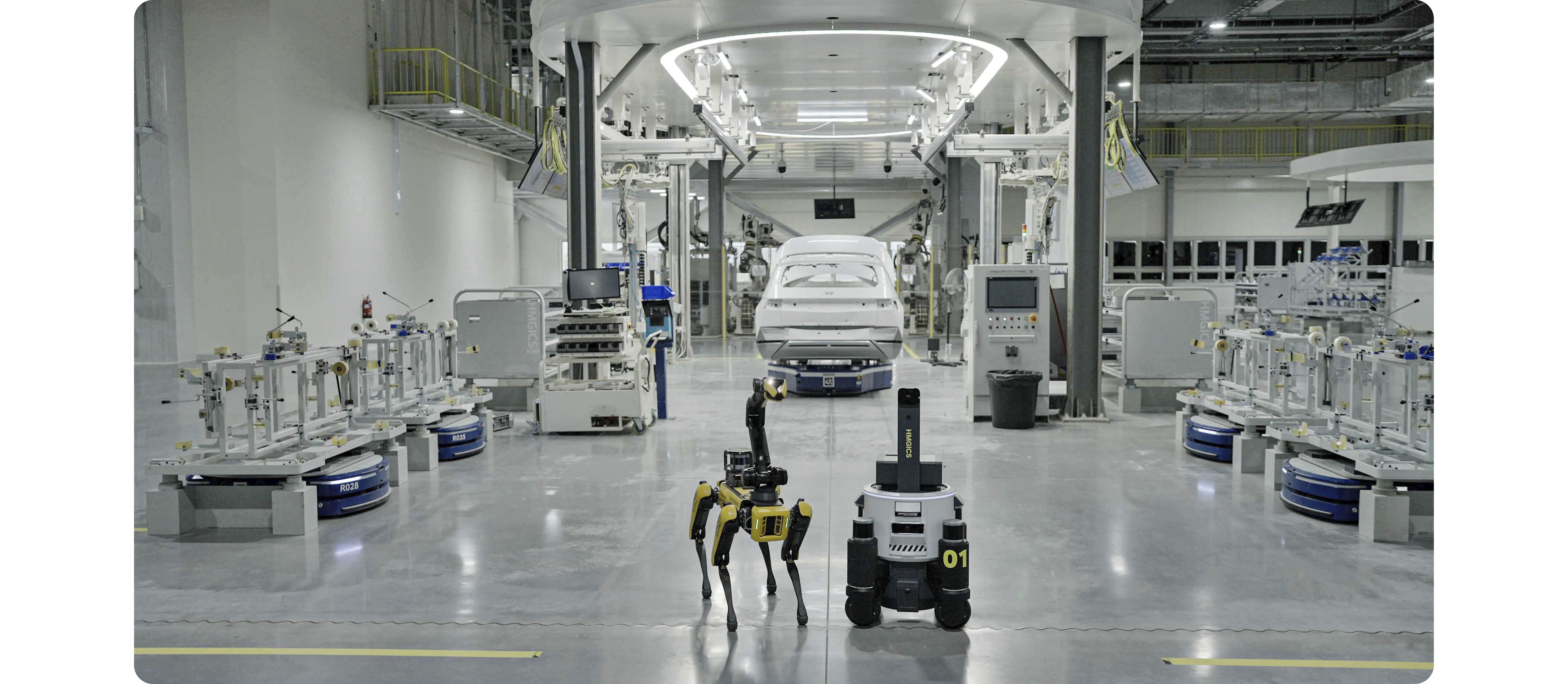
When introducing HMGICS’ representative robots, the performance of ‘AI Keeper’, a quality inspection robot, cannot be overlooked. HMGICS utilizes SPOT, a four-legged robot made by Boston Dynamics, to inspect assembly quality. The human workers and AI Keepers cooperate as if they have been working together for years. After a worker assembles various parts on a car, an AI Keeper approaches the car and takes photos of the assembly, which is then uploaded to the cloud and analyzed by vision AI to ensure that the assembly was done correctly.
As various work processes are gathered in one cell based on the conveyor production system, workers are able to focus on complex processes and are complemented by AI Keepers. In particular, when assembling the dark and complex interior of a car body, AI Keepers are able to catch errors that humans might not be able to see.
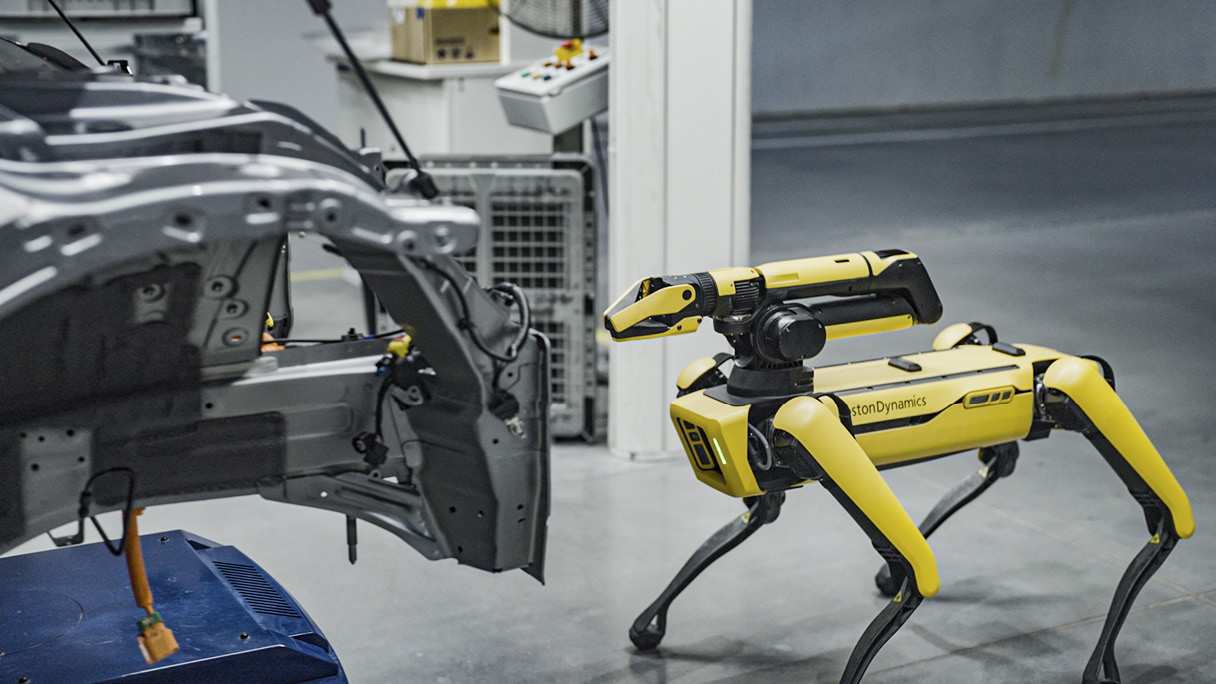

What sets the AI Keepers apart from other robots is their maneuverability and sophistication. The four-legged AI Keeper, which is also called a collaborative robot, is best suited to move in the same space as a human worker. The camera on the AI Keeper’s neck is flexible enough to easily shoot the interior of a car.
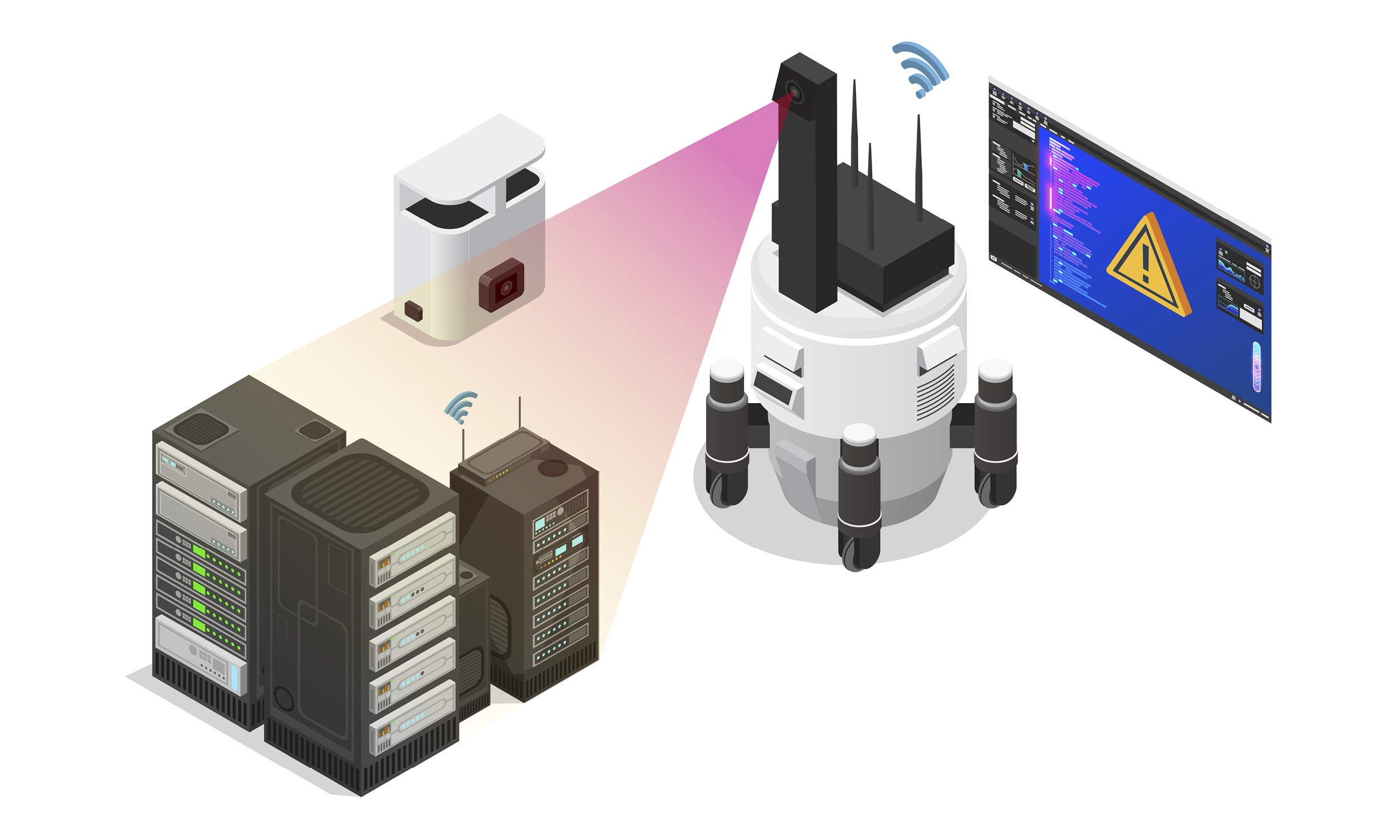
The last robot we will introduce is the safety inspection robot that inspects various equipment on the HMGICS production line. Utilizing Hyundai Motor Group’s Plug and Drive (PnD) module, the safety inspection robots roam freely across three floors of production lines and act as supervisors to inspect 64 facilities.
With two LiDAR sensors and four cameras each, the robots are autonomous, moving through spaces on their own at set times. The three cameras attached to the body of robots inspect the status of the production lines meticulously.
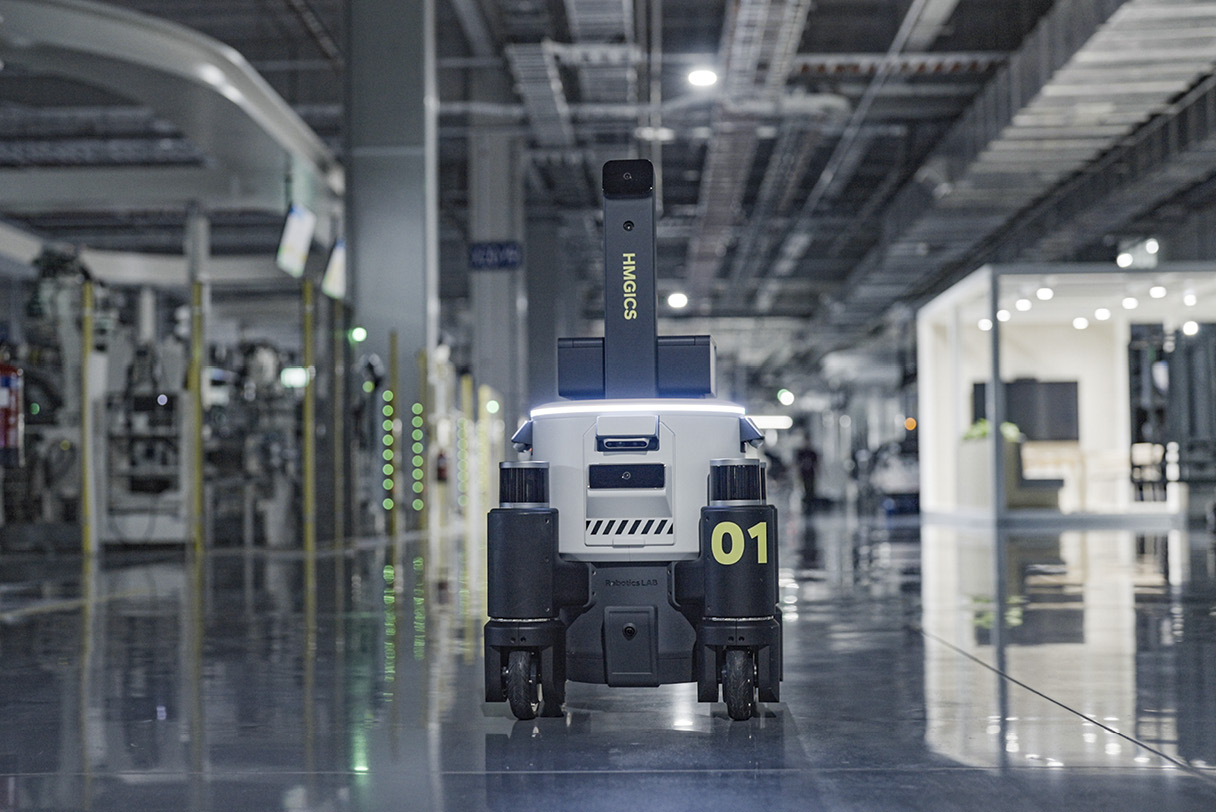

For example, if an equipment fault triggers a red lamp to light up, or a gauge needle moves outside of the normal range, the robot recognizes this and a-lerts the facility manager that something is wrong. In addition, it recognizes and reports solid parts — such as bolts and nuts that have fallen on the floor — as well as contaminants, creating a production site where technicians can work in a safe environment.

Hyundai Motor Group is constantly advancing the robotics technology required to produce a wide range of mobility products. In particular, we are focusing on developing robots that move precisely so that they can perform tasks smoothly that link robots and workers, and robots and robots.
For example, vision servoing is one of Hyundai Motor Group’s unique robotics technologies. This vision servoing is utilized by both logistics robots to drop off transported parts in the correct locations, and by production robots to pick up these transported parts accurately.
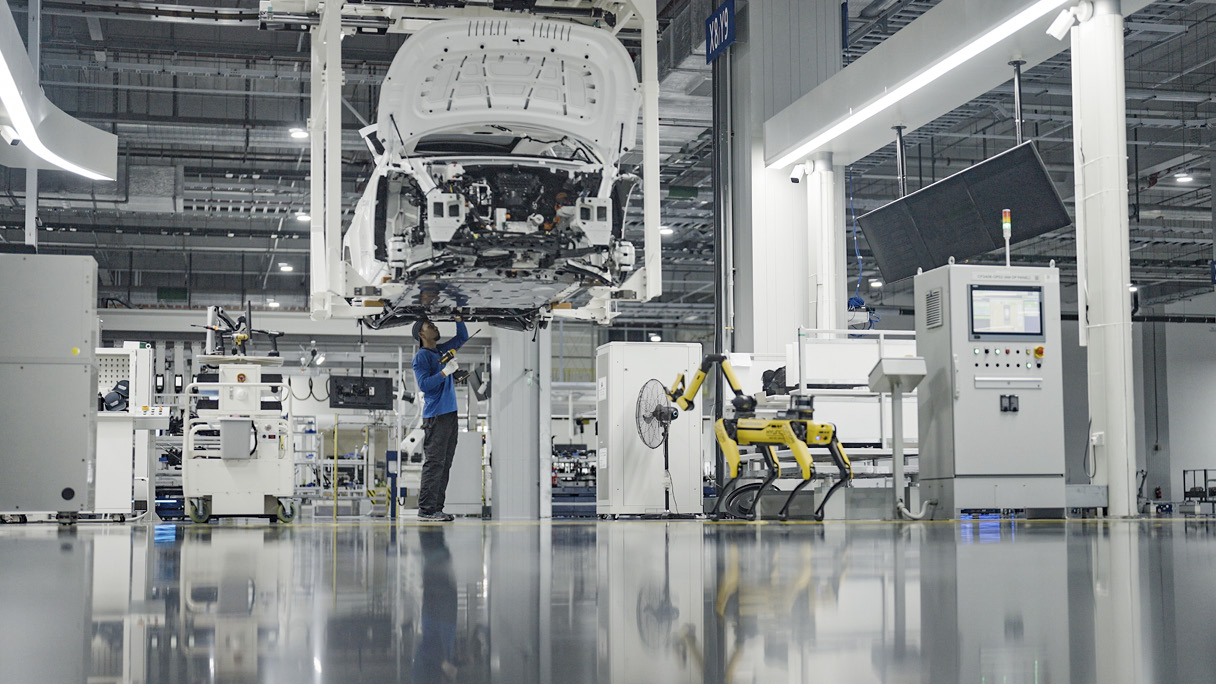

HMGICS also has an ideal ratio of humans to robots. Technicians and robots are assigned respectively to tasks that humans are good at and processes that robots can perform efficiently. Through this, both people and robots can showcase their respective strengths and maximize process efficiency and quality.
As such, HMGICS is focusing on the synergy that comes from cooperation between people and robots. This robotics technology that HMGICS continues to research and develop will be expanded to the Group’s global production base in the future.

Over this five-part series, we have taken an in-depth look at the cell production method, digital twin, AI, data, and robot technologies applied at HMGICS. Hyundai Motor Group will continue to make strides toward its vision of “making life more comfortable for people” based on these innovative technologies.
Hyundai Motor Group hopes that the variety of smart mobility we envision and the convenient and enriching mobility experiences that can be enjoyed in smart cities will become a reality as soon as possible.
The Full HMGICS Innovation Series
Part 1. The mobility factory without conveyor belts
Part 2. A twin factory in a virtual digital space