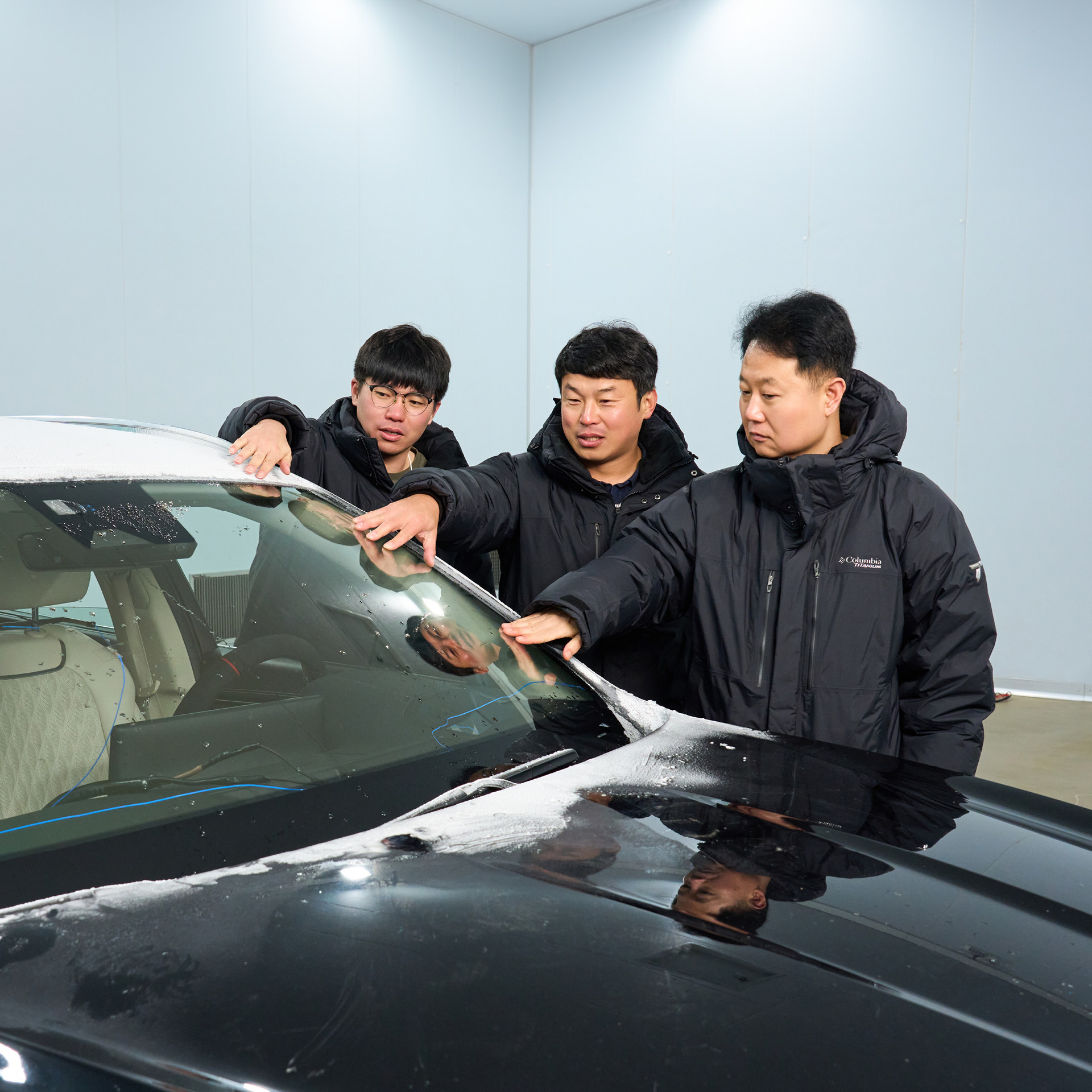




Hyundai Motor Group has consistently introduced cutting-edge technologies for future mobility, optimized for electric and autonomous vehicles. One such innovation is the newly developed metal-coating heated glass. This glass technology not only generates heat but also blocks solar heat energy, making it highly effective in managing external temperature conditions that could inconvenience vehicle users. As a result, it significantly enhances user convenience while also reducing the power consumption of the vehicle’s climate control system, contributing to more efficient operation of electric vehicles. Let's take a closer look at the features of this technology.

In regions with distinct seasons, like South Korea, temperature variations can reach up to 60°C throughout the year, leading to harsh winters and scorching summers. These extreme temperatures can cause issues such as frost or ice on windshield in winter or the interior heating up excessively in summer, causing discomfort for users. Traditionally, climate control systems were used to manage these issues, but their effectiveness was often limited depending on the situation.
For example, defrosting the windshield with a heater can take considerable time, as it not only takes a while for warm air to be generated from the heat source (whether engine waste heat or a PTC heater), but also because the thermal conductivity of air is low. Moreover, using the climate control system can direct air towards passenger’s faces, leading to dry skin, which can detract from the comfort of the driving experience.

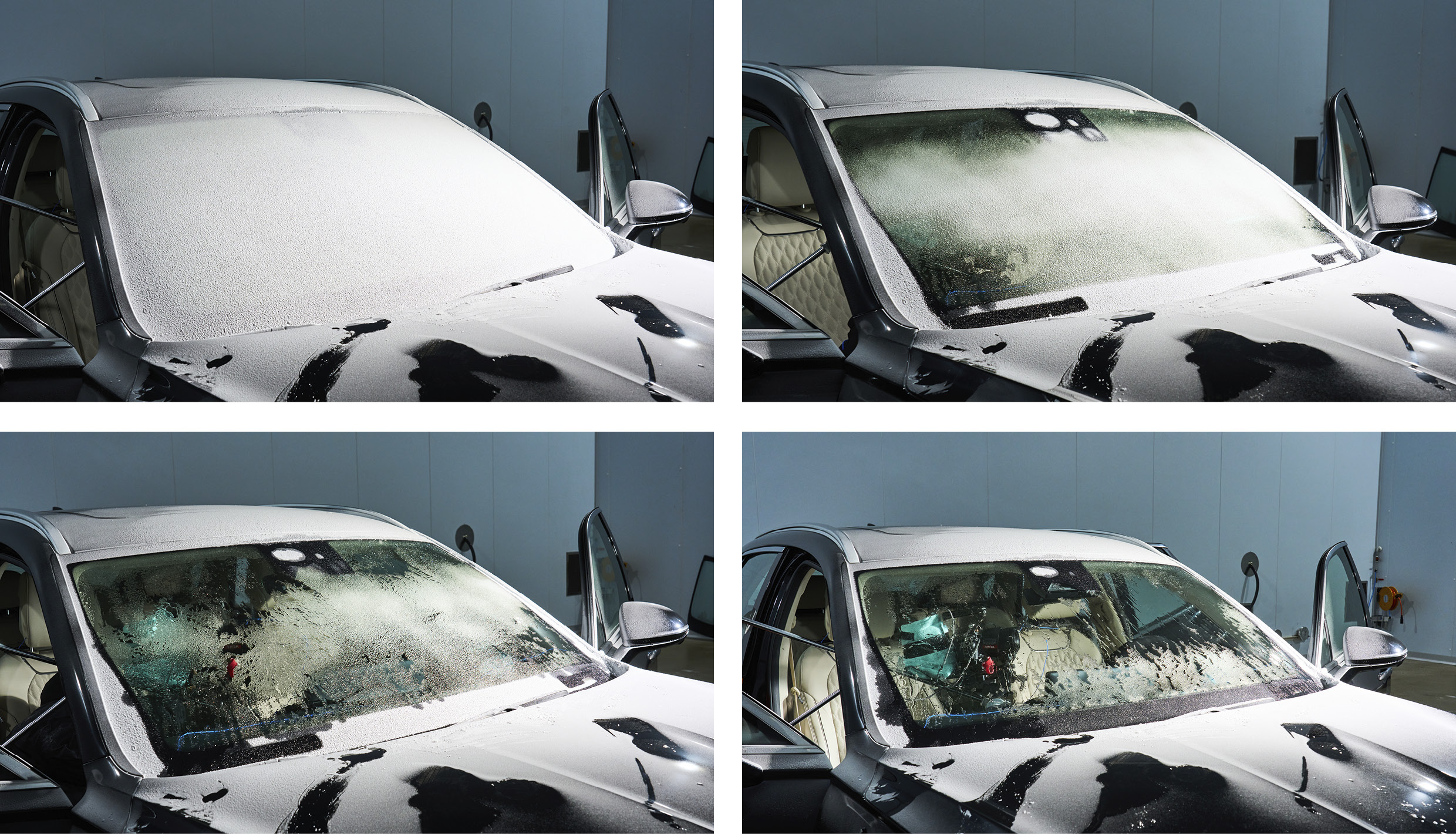
Such problems could pose challenges in the era of autonomous driving. Autonomous driving systems rely on sensors both inside and outside the vehicle to gather driving information, with vision sensors (such as cameras) and other data-gathering sensors attached to the windshield. If frost or moisture on the windshield is not quickly and thoroughly cleared, the autonomous driving functions may not operate smoothly. Hyundai Motor Group’s metal-coating heated glass, developed in line with the future of electric and autonomous mobility, effectively addresses these concerns.
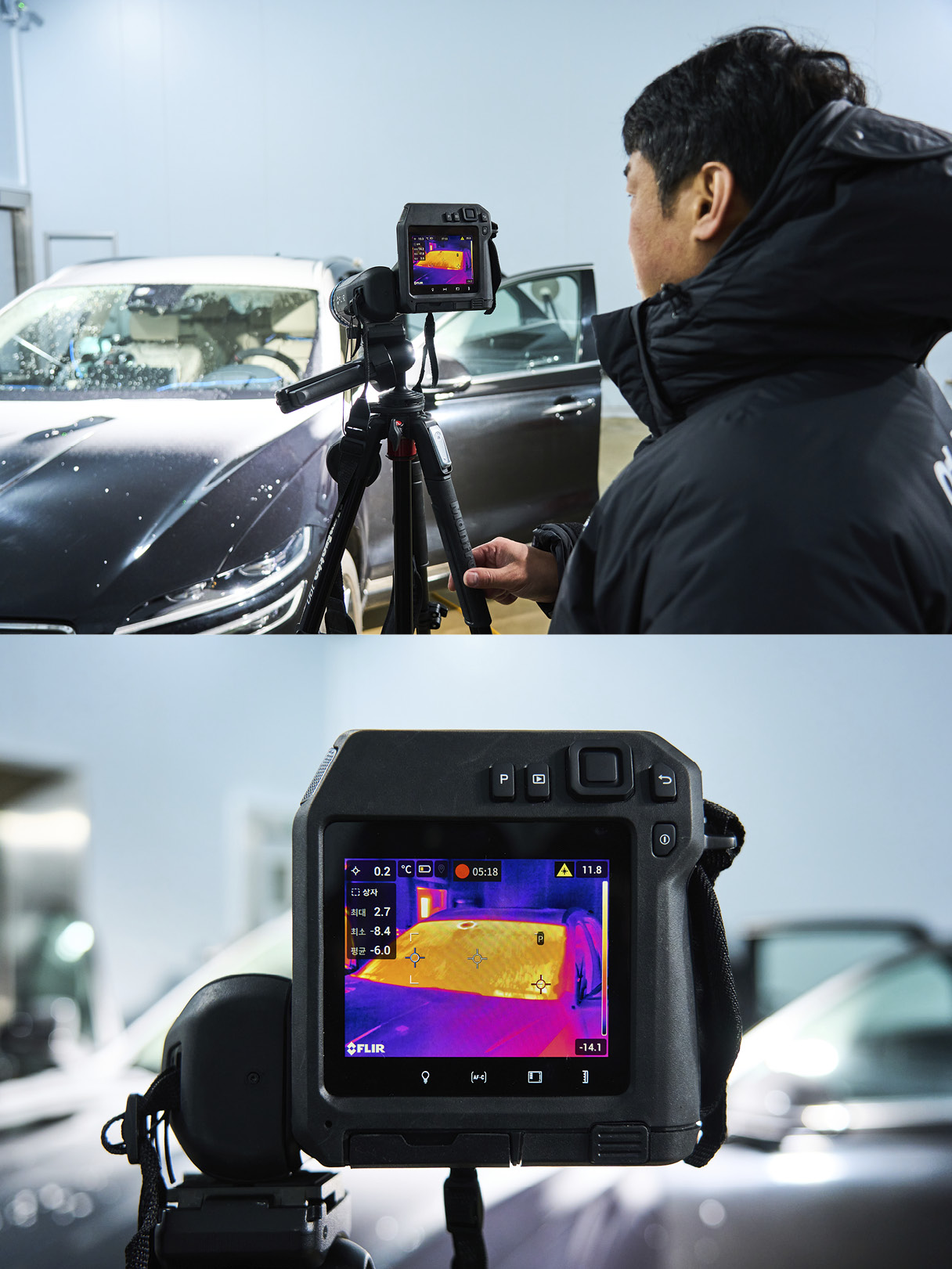

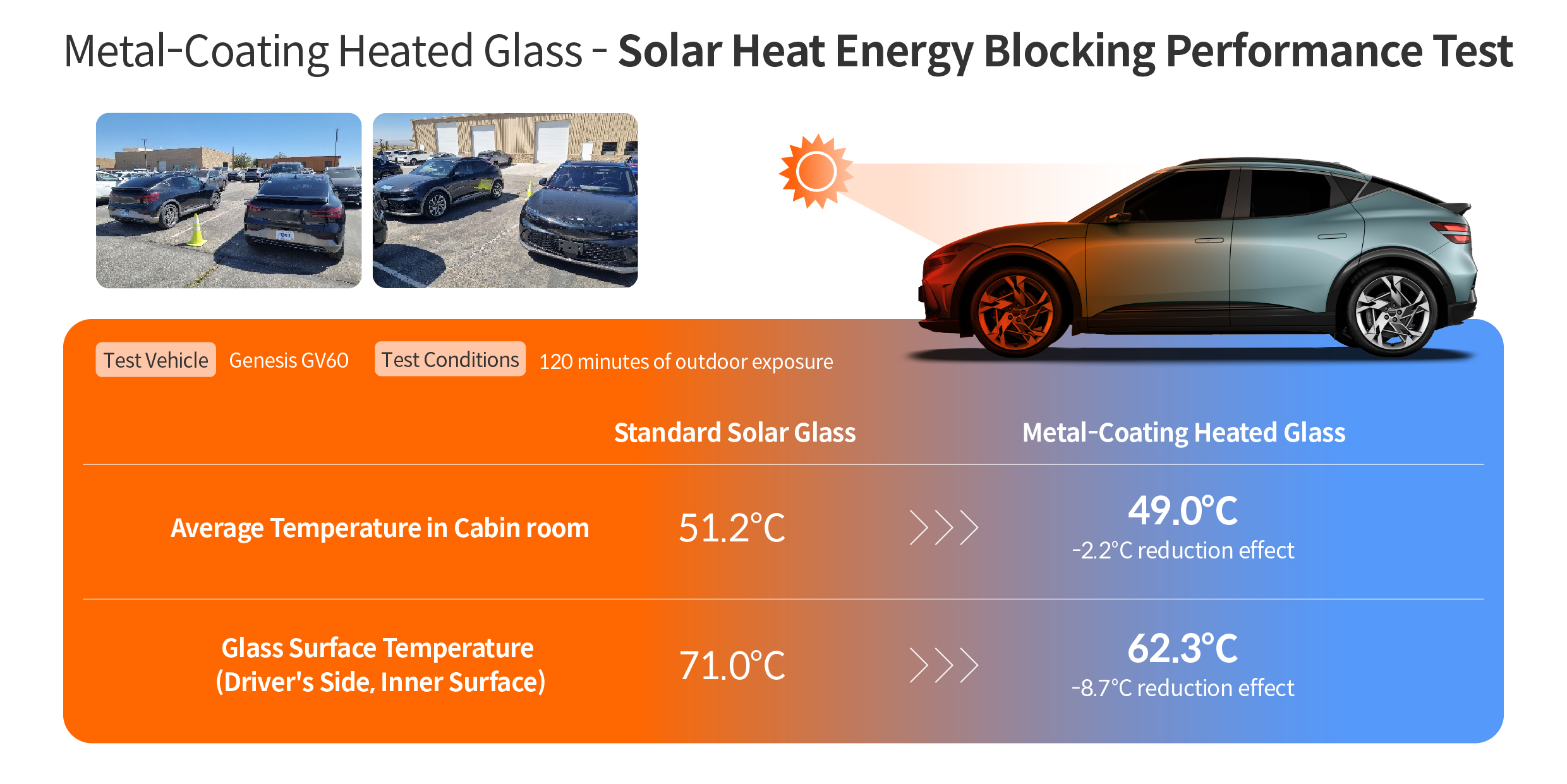
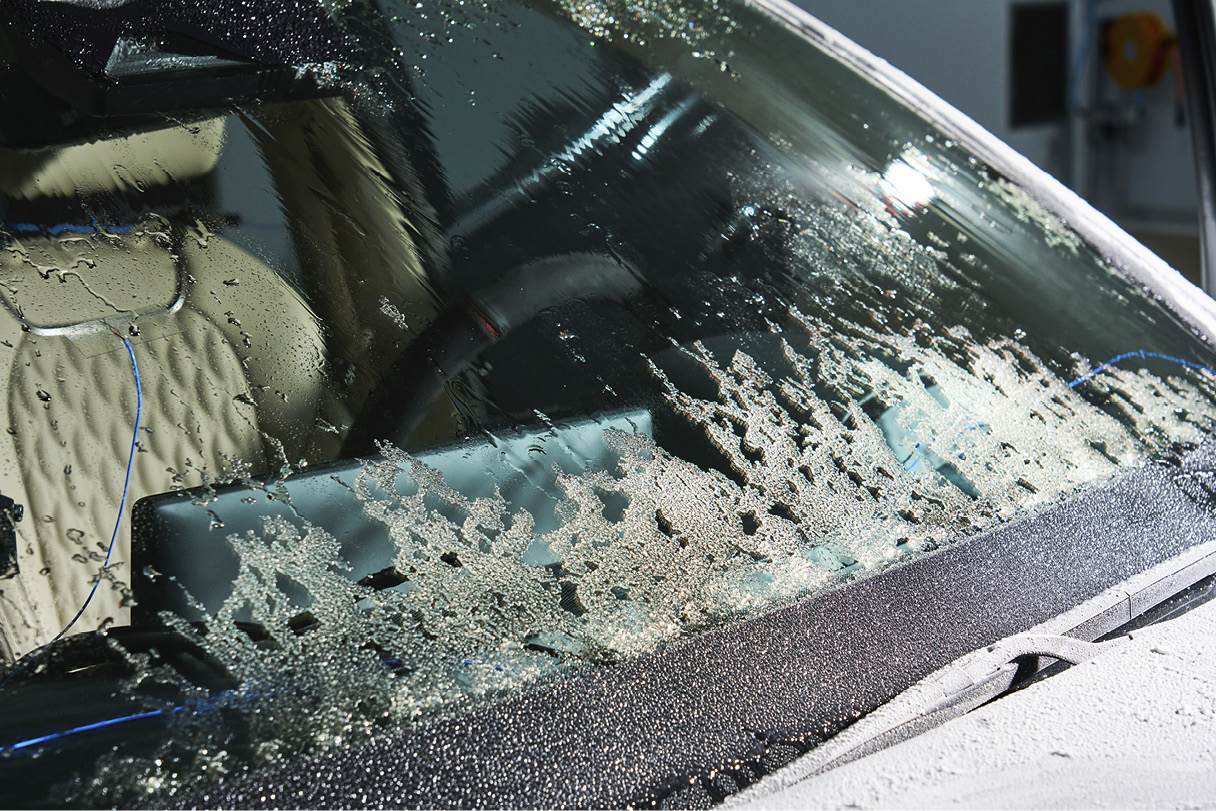
The most significant advantage of this technology is its superior defrosting and demisting performance, achieved by the glass generating heat on its own. The metal-coating heated glass can raise its temperature to completely remove frost within five minutes, even at -18°C. The secret to this impressive defrosting capability lies in the adoption of a 48V power system, which applies a higher voltage compared to the conventional 13.5V system.

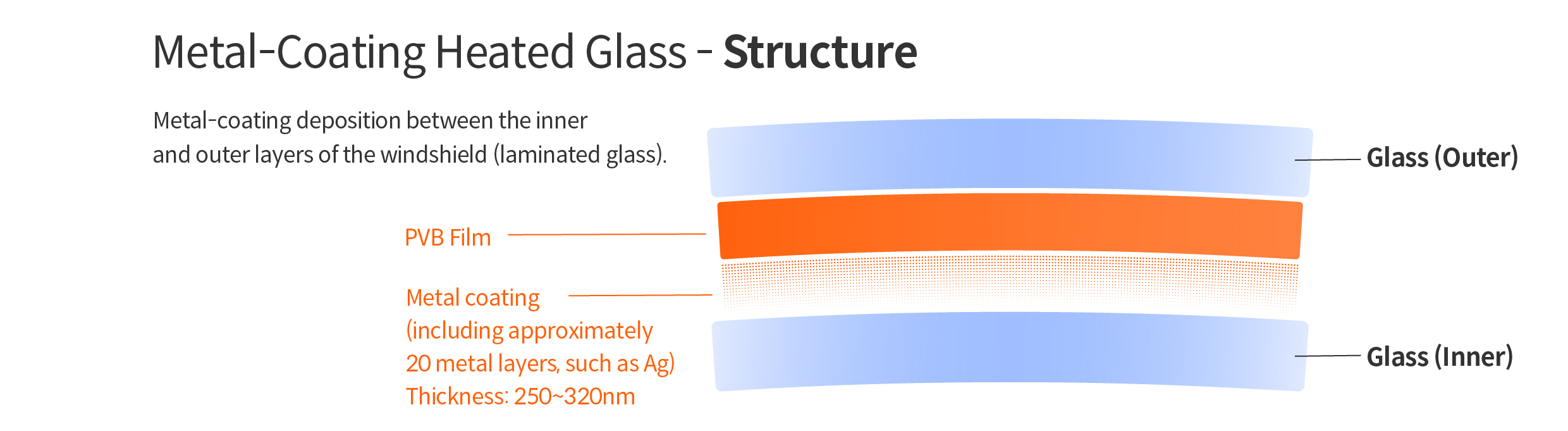
The core of this heating technology is the metal coating applied to the interior of the glass. This coating consists of approximately 20 metal layers, including silver (Ag), which, when electric current flows through it, functions as a heating element embedded within the windshield.
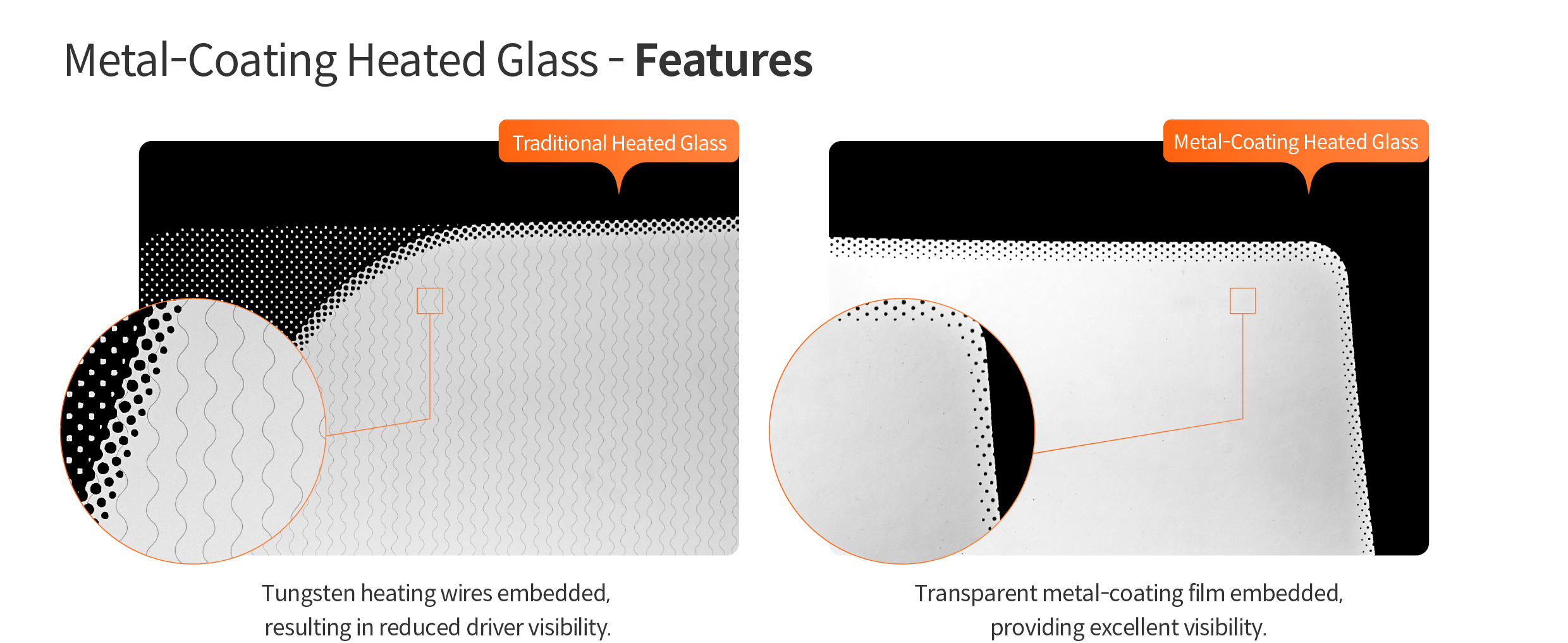
Another notable feature of metal-coating heated glass is its ability to provide an unobstructed view. Traditional windshields with embedded heating wires can obstruct the driver's view due to the visible tungsten heating wires. In contrast, metal-coating heated glass uses a transparent metal coating that guarantees a clear view without light reflection or distortion.
Metal-coating heated glass is not only beneficial in winter but also proves useful in summer. It effectively blocks solar heat energy, which is a major contributor to rising interior temperatures during hot weather. Solar heat energy is primarily transmitted through infrared radiation, among the various wavelengths of sunlight. By reflecting infrared radiation and emitting its own heat, metal-coating heated glass can block over 60% of total solar energy (according to ISO13837 standards), limiting the rise in interior temperature by up to 2-3°C.
*ISO13837: A standard for measuring the total transmittance of solar energy in automotive glass.
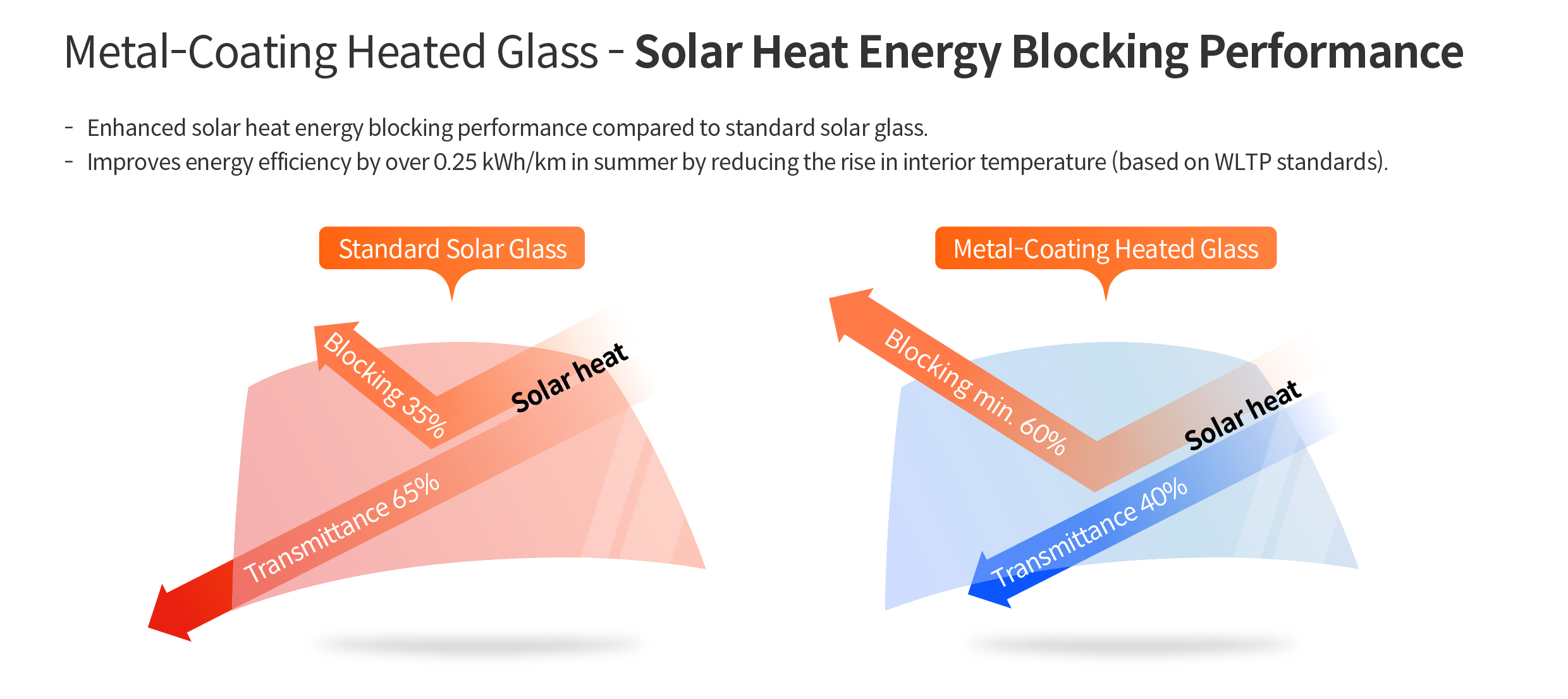
This technology stands out even when compared to heat-blocking tint films. Most tint films with similar heat-blocking properties have a visible light transmittance of less than 70%, below the regulation. Consequently, using such films can impair the driver’s view in poor weather conditions, or hinder the timely detection of infants left in the vehicle. However, the visible light transmittance of metal-coating heated glass exceeds 70%, meeting legal requirements while providing a bright and clear view that ensures the safety of both drivers and passengers.
Moreover, metal-coating heated glass does not suffer from the communication issues often caused by heat-blocking tint films. The metal components in such films can interfere with various signals inside the vehicle, such as those from electronic toll collection devices, apartment entry cards, mobile phones, and GPS, leading to malfunctioning devices. To address this, the metal-coating heated glass leaves areas where heating is not required uncoating, and applies pattern processing to the coating areas, ensuring signal reception performance comparable to that of regular glass.

In the future mobility era, the utility of metal-coating heated glass is expected to gain even more attention. By applying this technology, it’s possible to eliminate the air vents on the upper crash pad traditionally used for defrosting and demisting, significantly improving design flexibility for the upper crash pad. This can pave the way for innovations such as full windshield head-up displays and large augmented reality navigation systems.
Additionally, applying metal-coating heated glass in electric vehicles can reduce power consumption. The defrosting performance alone saves up to 10% of the power typically used by conventional heaters, and the heat-blocking function can further reduce air conditioning power consumption. In summary, metal-coating heated glass is a versatile technology offering excellent defrosting and demisting performance, superior heat-blocking capabilities to control interior temperature, energy savings, and a safer driving environment.

Hyundai Motor Group anticipates that metal-coating heated glass will not only enhance user comfort and convenience but also improve vehicle safety in extreme cold regions, allow for more flexible interior design layouts, and increase the energy efficiency of electric vehicles. The part leader Jeong Gi-heon and the senior research engineer Lee Kang-hee from MLV Exterior Design Team 1 explained in detail how metal-coating heated glass can make our daily lives more comfortable and convenient.

Q: What are the features of metal-coating heated glass, and how does it compare to existing technologies?
Senior Research Engineer Lee Kang-hee: In extremely cold regions like Northern Europe and Canada, some vehicles use heated glass with tungsten wires embedded in the windshield. These systems operate on a 13.5V power system, which results in limited defrosting and demisting performance, and the visible tungsten wires can obstruct the driver’s view. However, our metal-coating heated glass is a highly competitive technology, offering a wide range of functions and superior performance.
We have adopted a 48V power system, the first of its kind globally, which raises the glass temperature much faster than the traditional 13.5V system, delivering excellent defrosting and demisting performance. Instead of tungsten wires, we use a transparent metal coating as the heating element, providing a clear, undistorted view. Additionally, our tests have shown that this glass can block solar heat energy, reducing interior temperature increases by up to 2-3°C during the summer.

Q: How much has performance improved with the application of the 48V power system?
Part leader Jeong Gi-heon: The 48V power system is optimized for electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles, allowing them to utilize the high-efficiency power from high-voltage batteries. With this system, metal-coating heated glass can raise its temperature to as high as 75°C from room temperature. While the system can achieve even higher temperatures mechanically, we’ve capped it at this level to ensure passenger safety. In our tests, this system demonstrated its ability to completely remove frost within five minutes at -18°C. By comparison, a 13.5V power system under the same conditions takes over 15 minutes to achieve similar results.
Q: What advantages does metal-coating heated glass offer compared to heat-blocking tint films?
Senior Research Engineer Lee Kang-hee: Heat-blocking tint films are generally divided into non-reflective and reflective types. Non-reflective films absorb solar heat energy and re-radiate it both inside and outside the vehicle, while reflective films use metal coatings to reflect solar heat, providing superior heat-blocking performance. Metal-coating heated glass operates on the same principle as reflective films in terms of solar heat energy blocking but meets regulation by ensuring a visible light transmittance of over 70%. Additionally, to address the signal reception issues commonly associated with reflective films, we designed the metal coating so that it is applied only where heating is needed, ensuring signal reception performance equivalent to that of standard glass.

Q: How significant do you expect the role of metal-coating heated glass to be in the future mobility era?
Part Leader Jeong Gi-heon: The competitiveness of electric vehicles is closely tied to thermal management technology. By managing thermal energy efficiently, electric vehicles can maximize their convenience features and extend their driving range. Therefore, metal-coating heated glass is poised to become a key technology in the electric vehicle era, offering significant energy and time savings. We look forward to advancing into the future mobility era with metal-coating heated glass, which provides a comfortable interior environment and ensures a safer driving experience.
Video by Nam Do-yeon and Lim Woo-jin
Photography by Cho Hyuk-su