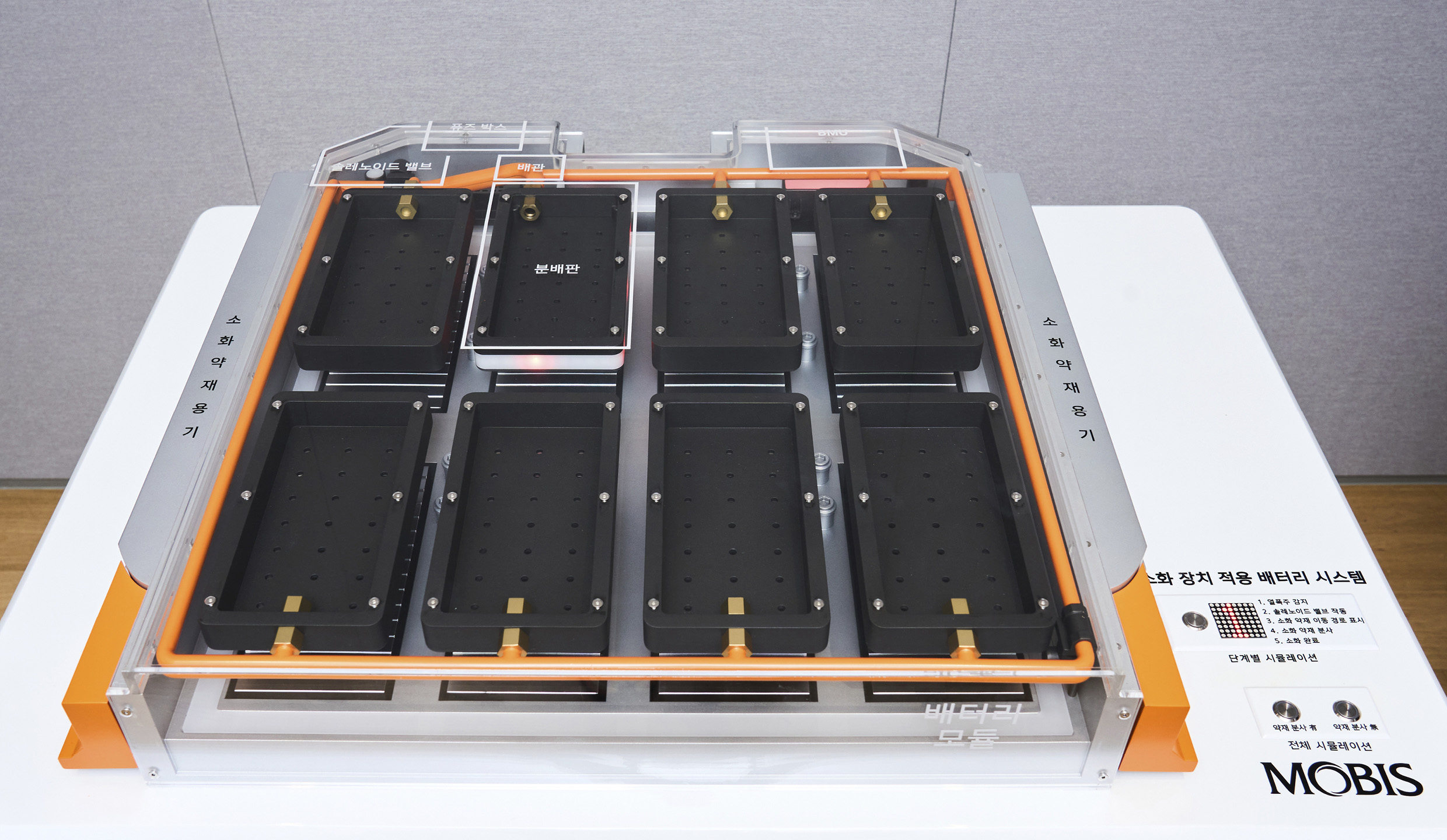





Hyundai Mobis has developed a new technology that detects battery cell anomalies and instantly extinguishes any fire at the affected location only. The system targets the exact cell experiencing thermal runaway, automatically releasing fire suppressants to cool it down and prevent the fire from spreading to neighboring cells. This breakthrough effectively halts thermal propagation before it becomes a major hazard.
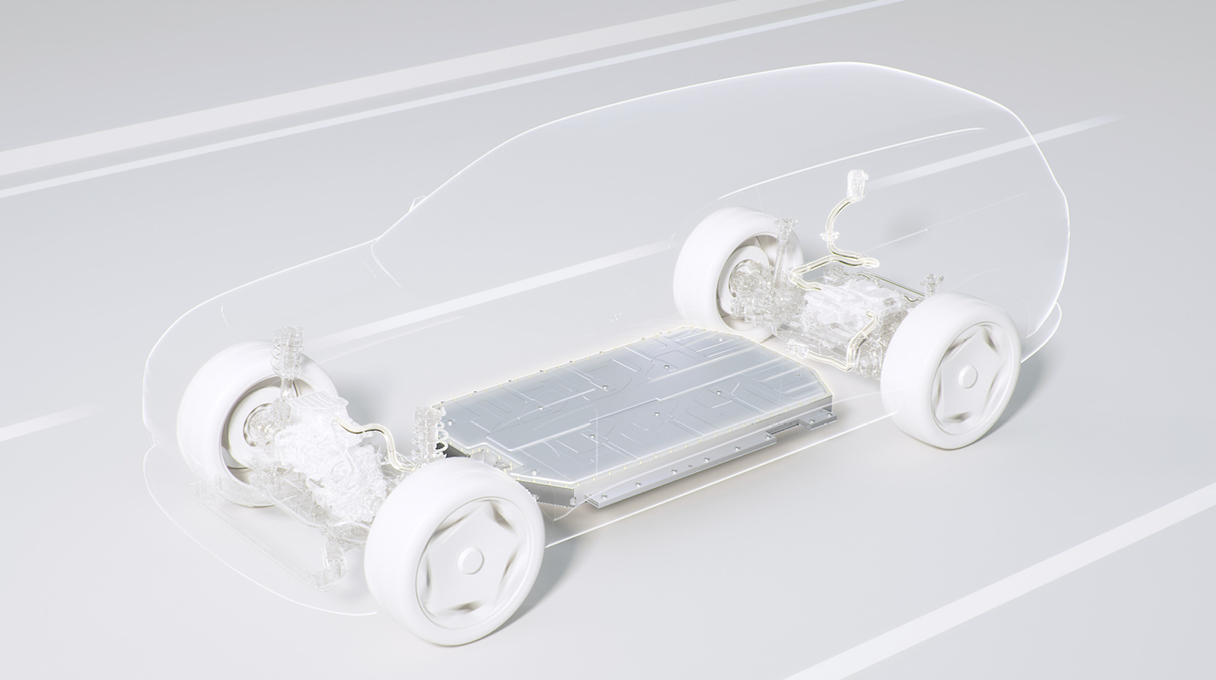
Countries leading the EV transition—such as those in Europe, China, and India—are now mandating that thermal runaway must be delayed by at least five minutes after a cell fire. Starting next year, China will go even further, enforcing regulations to completely block heat transfer between cells. Hyundai Mobis' cell-level fire suppression battery system meets these challenges head-on. We spoke with Seung-jun Lee, a research engineer from the Hyundai Mobis EV-BSA (Electric Vehicle–Battery System Assembly) development team, to learn more about this cutting-edge technology.
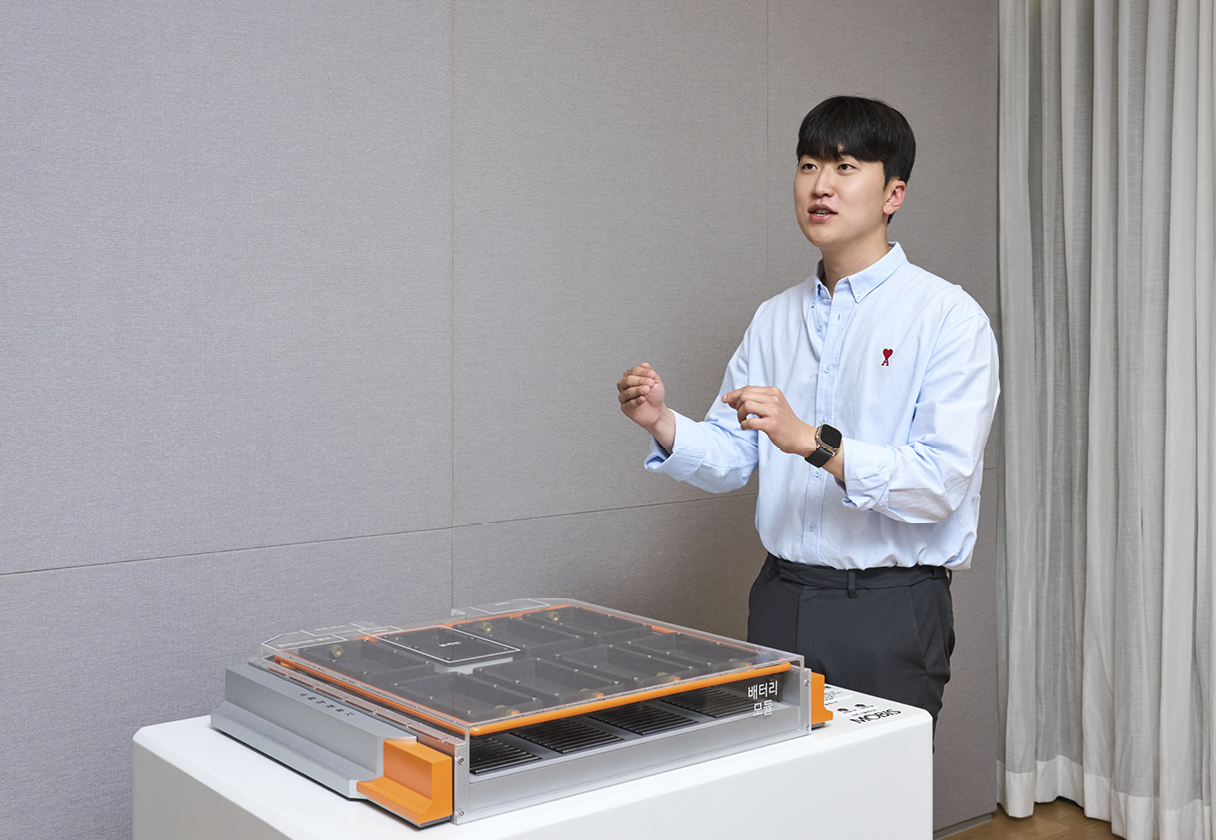

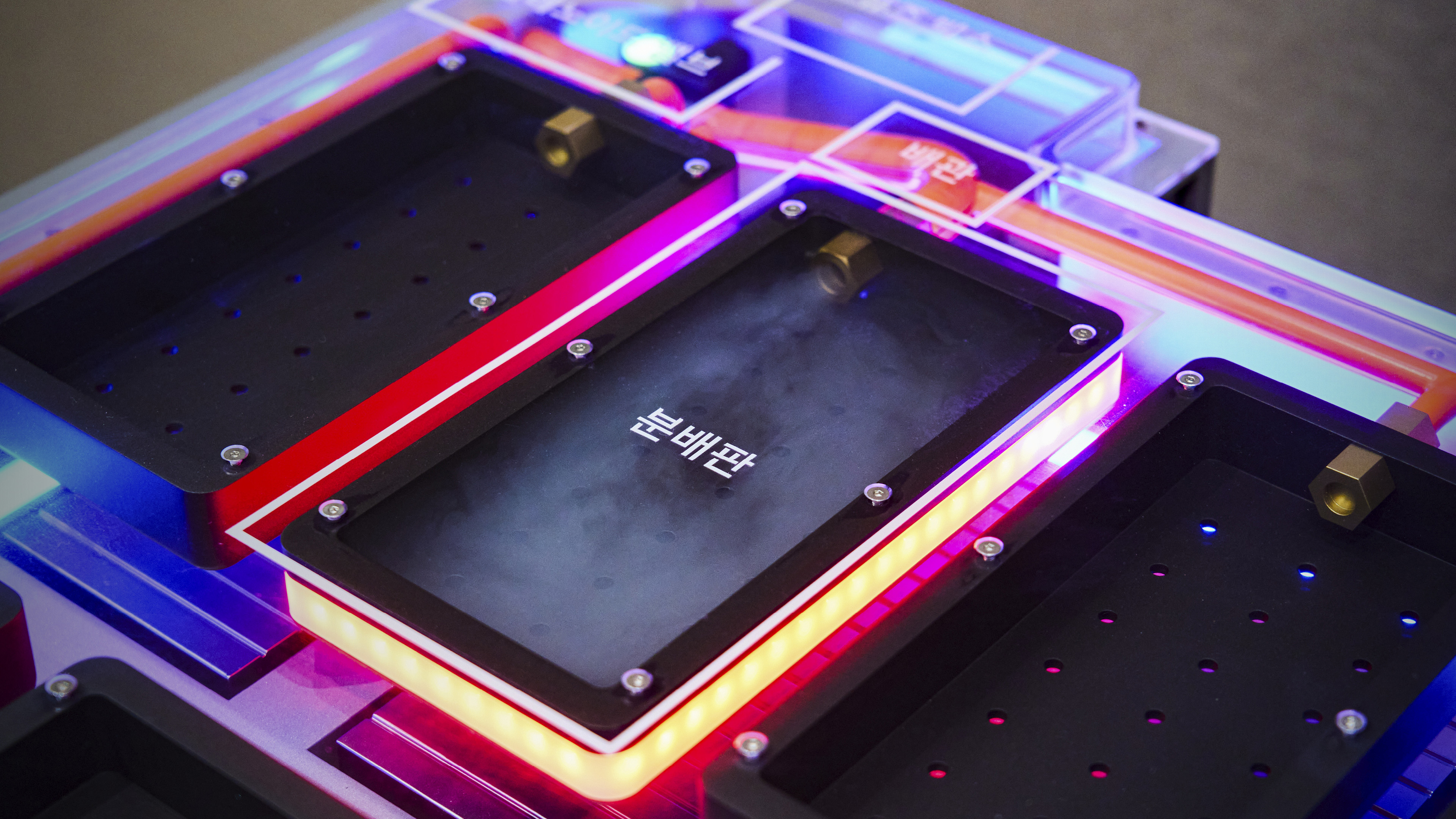
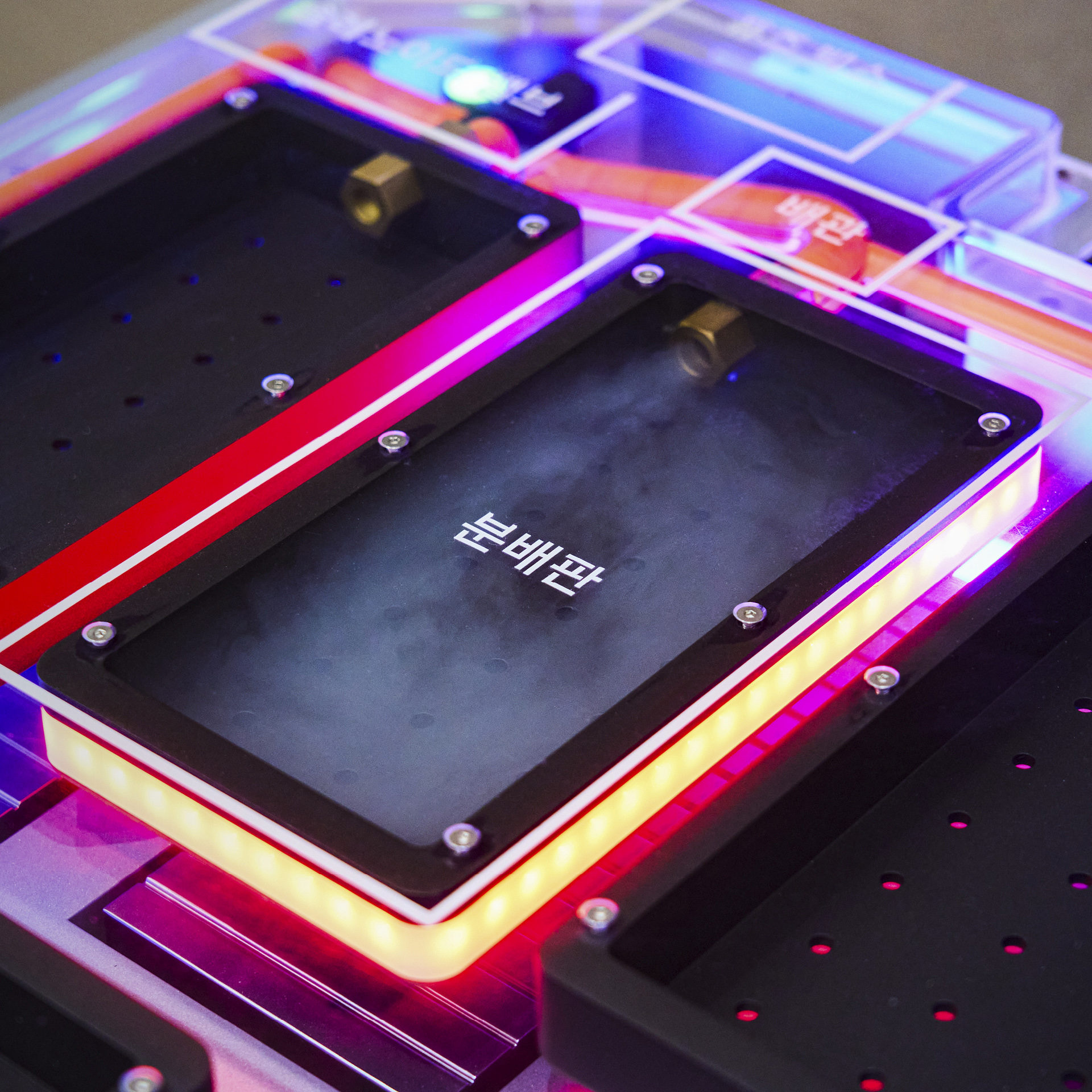
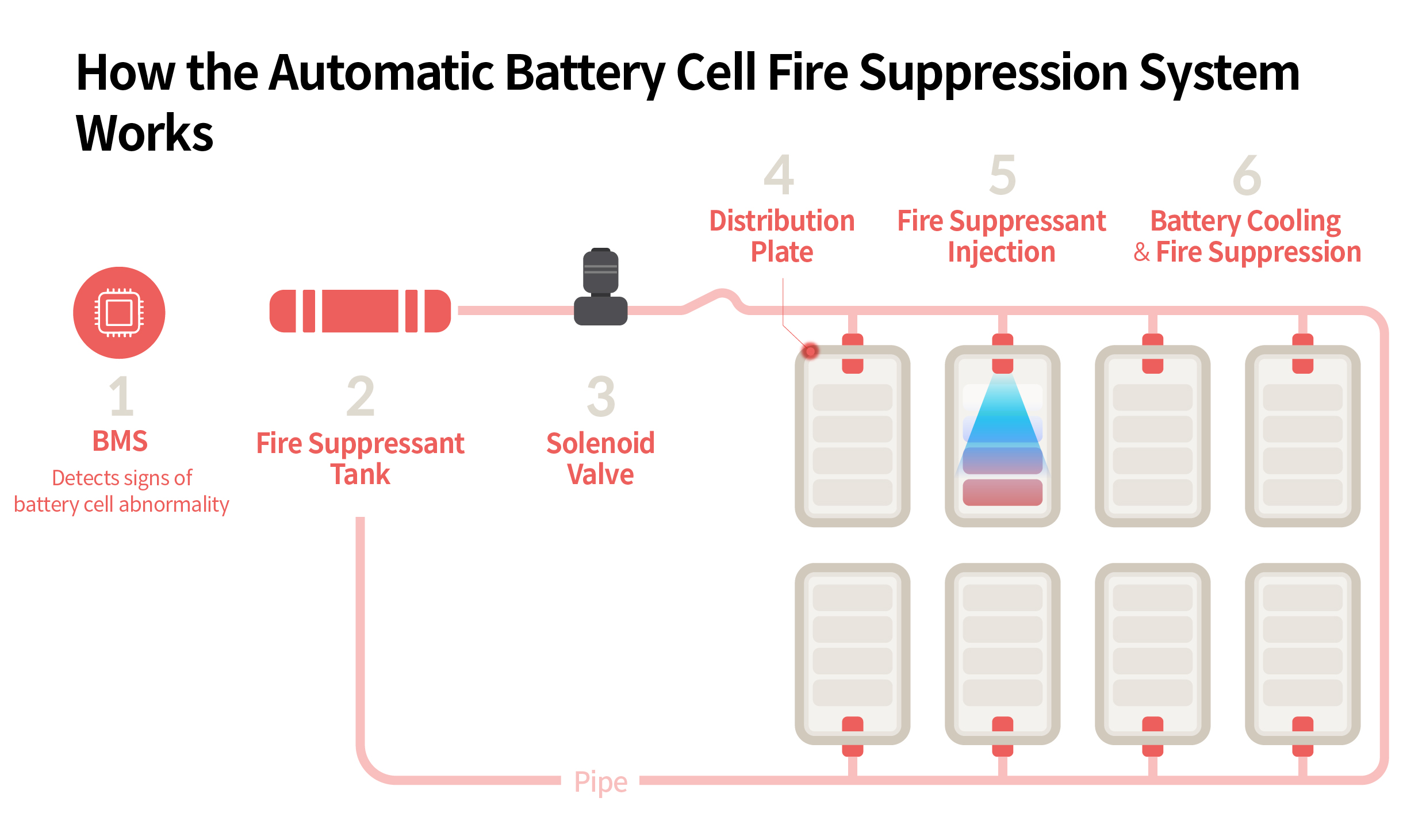
The standout feature of this new system is its pinpoint accuracy. When an issue is detected, fire suppressants are released only at the affected module—not throughout the entire battery pack. This precision is made possible through a combination of smart hardware and software, including a Battery Management System (BMS), a compact suppressant tank, and a system of valves and distribution plates. Seung-jun Lee emphasized that minimizing the size of the fire suppression hardware was key:
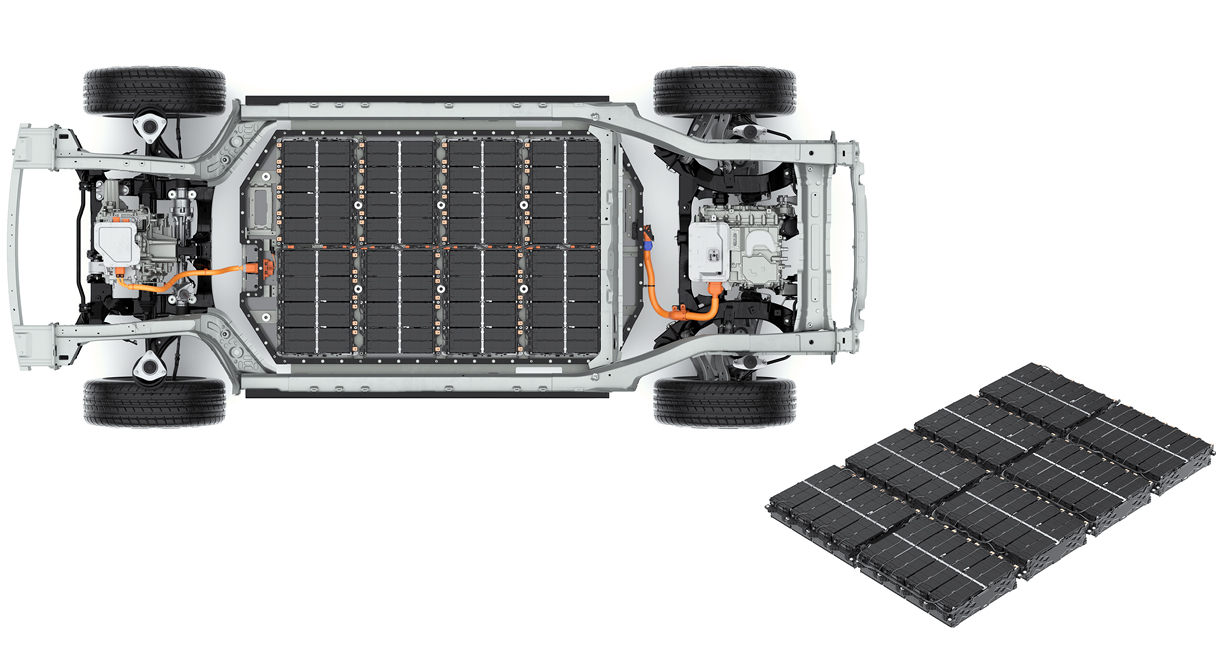
“Today’s EV battery systems aim to deliver more capacity while taking up less space,” says research engineer Seung-jun Lee. “That’s why we focused on downsizing the hardware needed for the suppression system, without compromising its effectiveness. Our goal was to create a compact structure that could fit into the existing battery pack layout.”
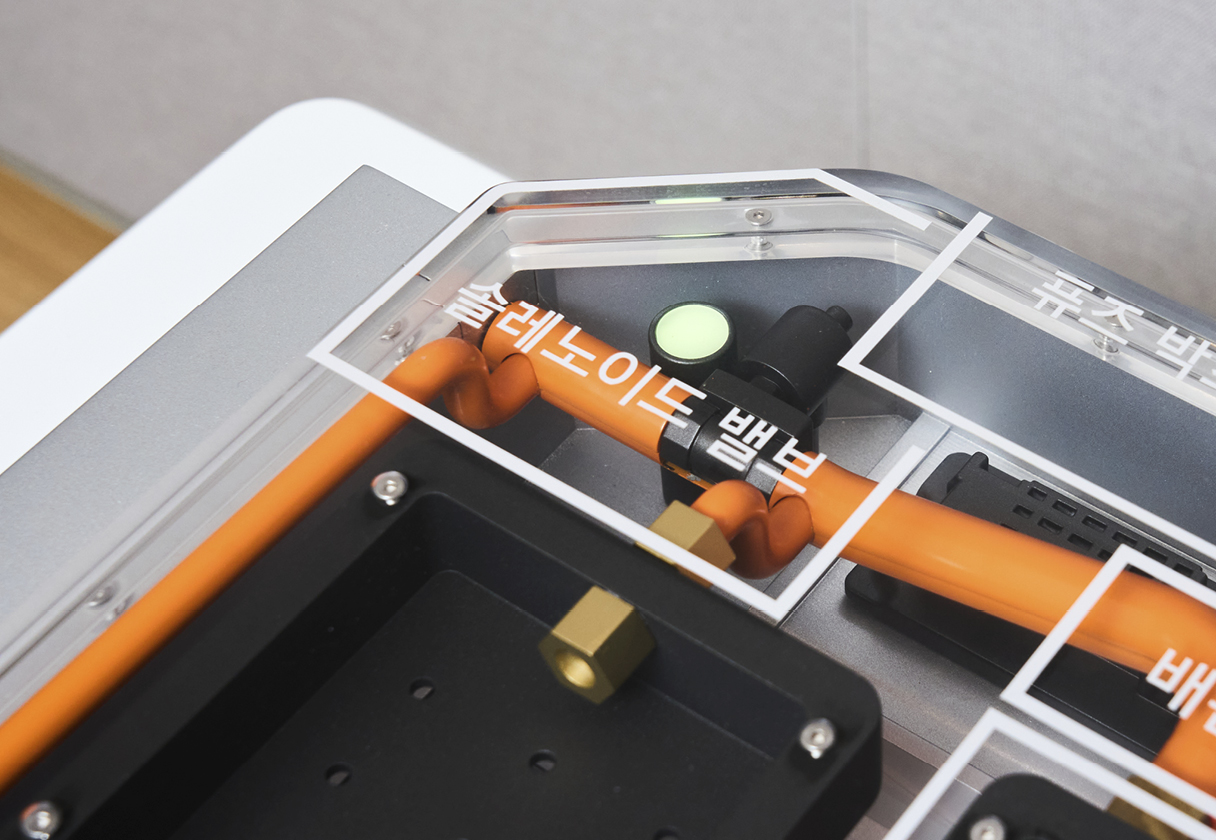
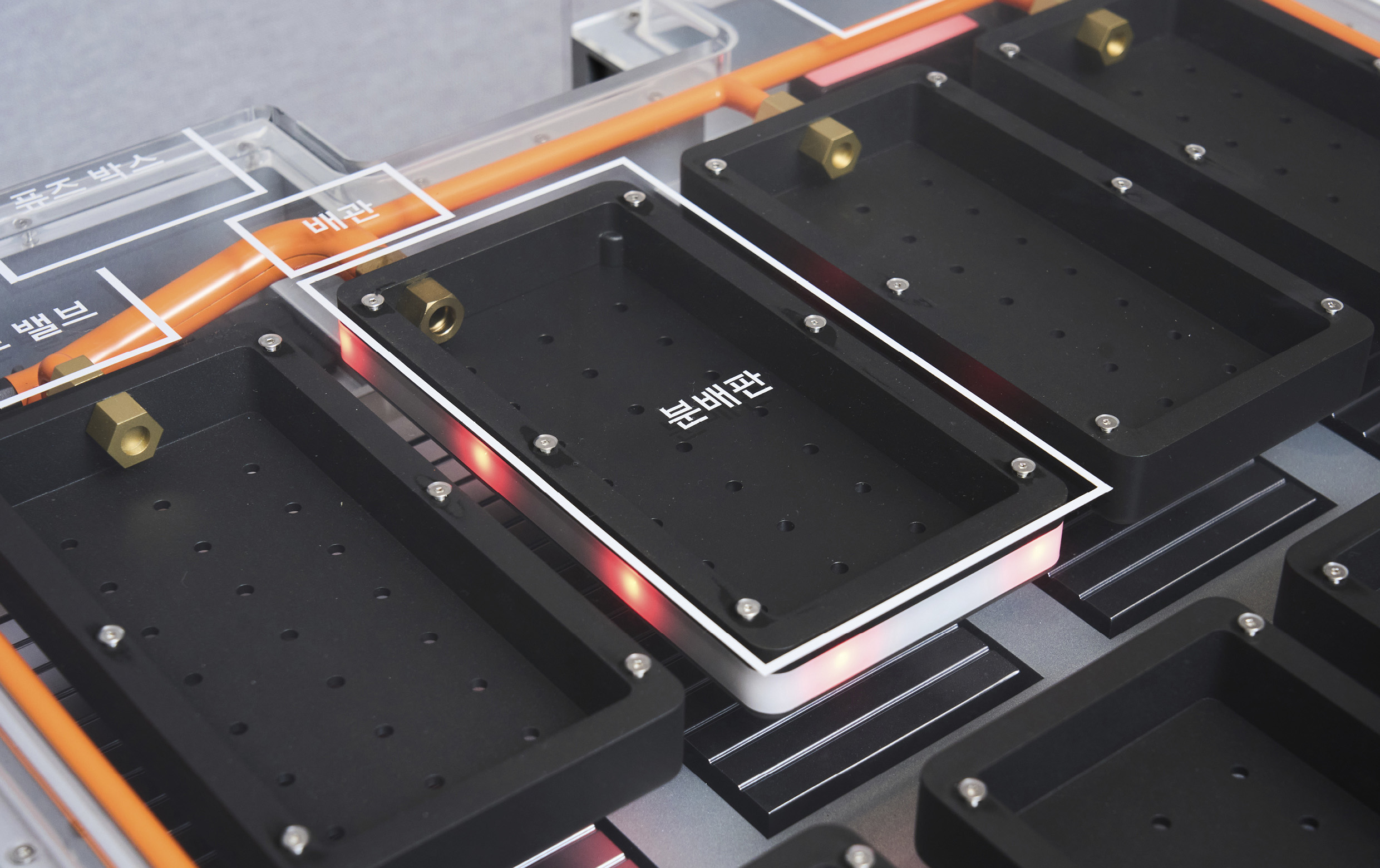

The BMS analyzes real-time sensor data from within the system—monitoring temperature, voltage, and internal pressure—to identify any signs of abnormal behavior. This allows it to pinpoint exactly which battery cell is experiencing trouble. The hardware includes a tank filled with fire suppressant and a series of distribution plates located above each battery module, all connected via internal piping housed within the battery enclosure.
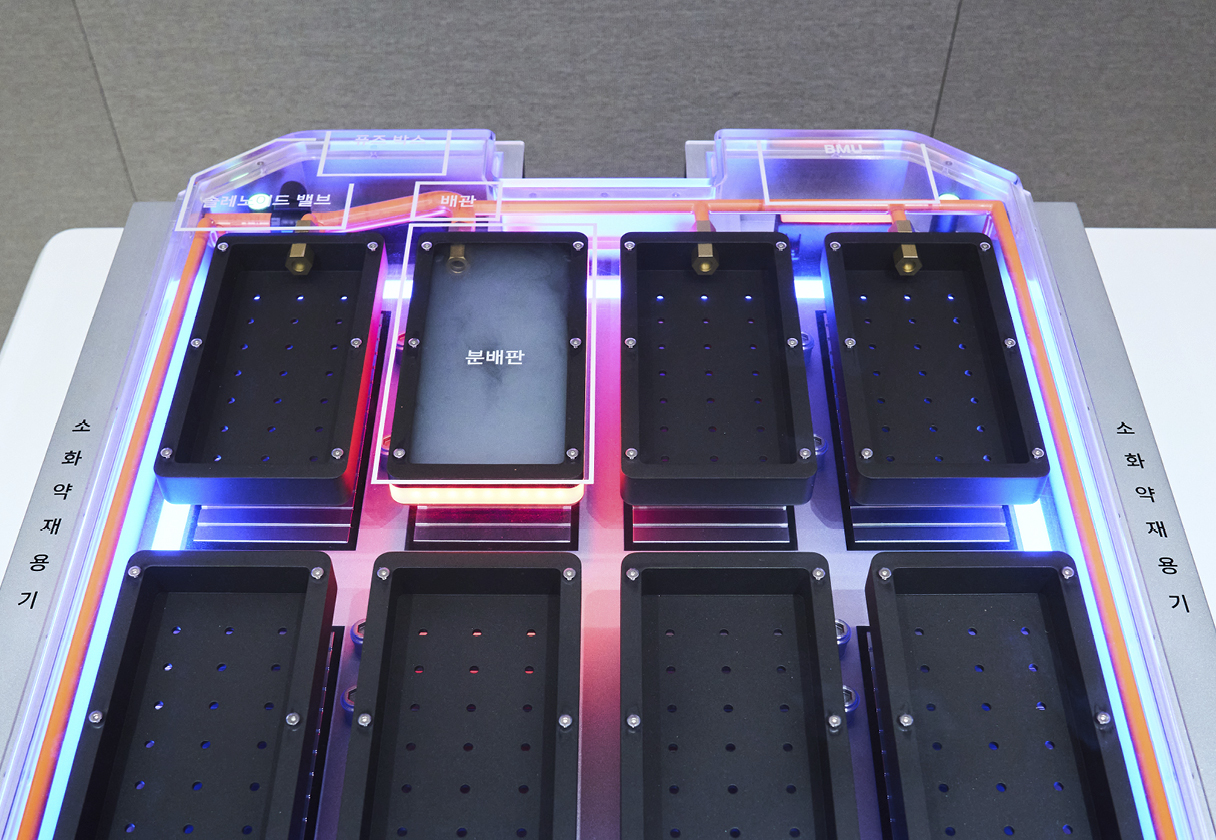
Once the BMS detects a fault, the system controls the valves to route fire suppressant directly to the distribution plate above the affected module. The suppressant flows into the module and cools down the battery cell—or extinguishes the fire if it has already started.
Hyundai Mobis has applied for three domestic and international patents related to the battery case and fire suppression technology. So why didn’t the team just opt for the seemingly simpler method of spraying suppressant across the entire battery system?
Seung-jun Lee explains: “Our priority was user safety. The best way to ensure full suppression was to concentrate the suppressant precisely where it’s needed. Since there’s a limit to how much suppressant can be stored in the battery system, we designed it to maximize effectiveness with targeted delivery.”
Though hard to spot in the mock-up display, the distribution plate is remarkably thin—an intentional design choice to minimize space usage inside the battery system. This allows automakers to maintain range by fitting in as many cells as possible. While the tank and piping still need to be installed, the system avoids requiring a complete redesign of the battery structure, making it compatible with battery packs already used in many EVs.

Lee continues: “The number of distribution plates and the amount of fire suppressant can be freely adjusted. That means it can be applied to any battery architecture, including Cell-to-Pack systems that skip the module stage altogether. This is a world-first application with no global precedent. Hyundai Mobis is proud to be leading the way in advancing EV safety.”
The automatic suppression system isn’t just reactive—it can proactively cool cells before a fire starts. Because the BMS continuously monitors each cell’s condition in real time, it can trigger the suppressant early enough to prevent thermal events before they occur.

“Today’s EV batteries store significantly more energy than older generations. That’s why we now enjoy longer driving ranges and features like V2L (Vehicle-to-Load) to power external devices,” Lee explains. “But more energy also means more heat. And that heat, if mismanaged, can lead to bigger fires. That’s why we’re investing in advanced thermal management technologies to make batteries safer for everyone.”
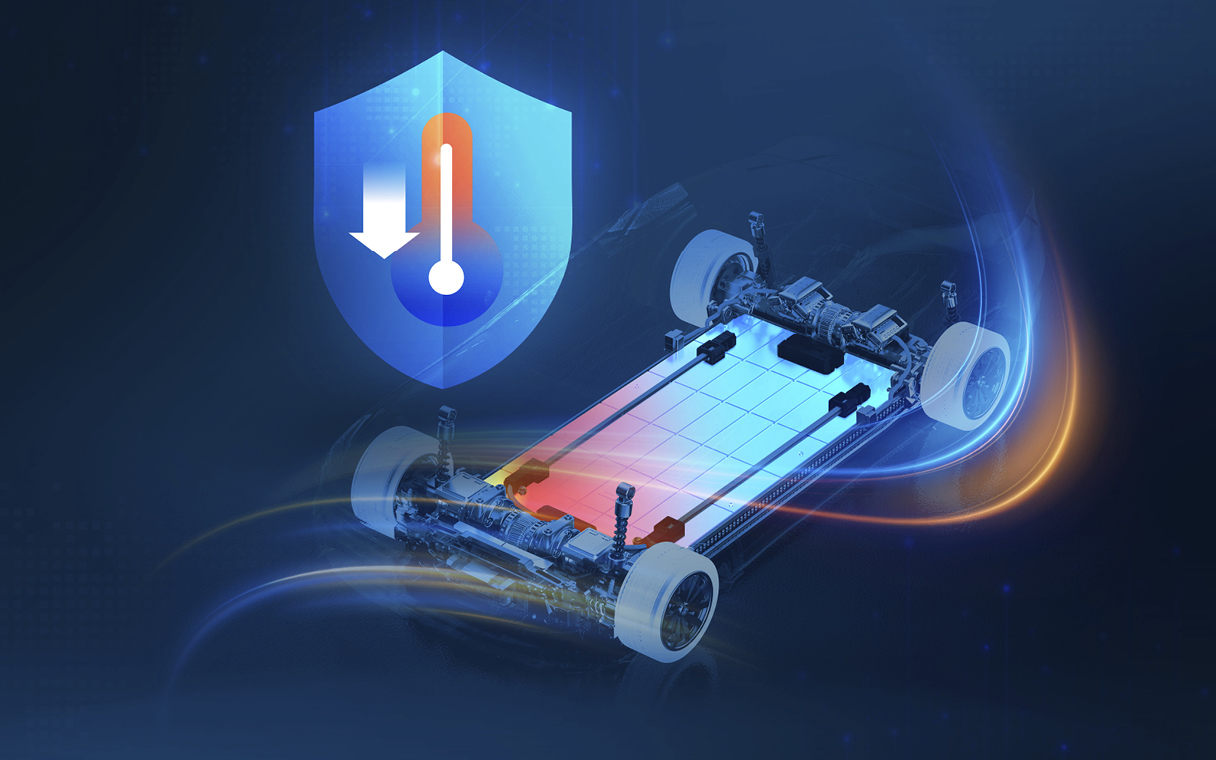

Last year, Hyundai Mobis developed a vibration-based heat pipe system designed to prevent battery overheating during fast charging. The system uses aluminum alloy and refrigerant to cool cells by transferring heat away from the battery. It’s one more way Hyundai Mobis is enhancing battery safety by controlling heat buildup inside the pack.

As a mobility solutions provider, Hyundai Mobis continues to lead the way in creating advanced, integrated battery systems that combine smart hardware and intelligent software. Its push for safer electric vehicles is more than just innovation—it’s a commitment to public safety. Hyundai Mobis is driving mobility forward, one breakthrough at a time.
Photography by Hyuksoo Cho